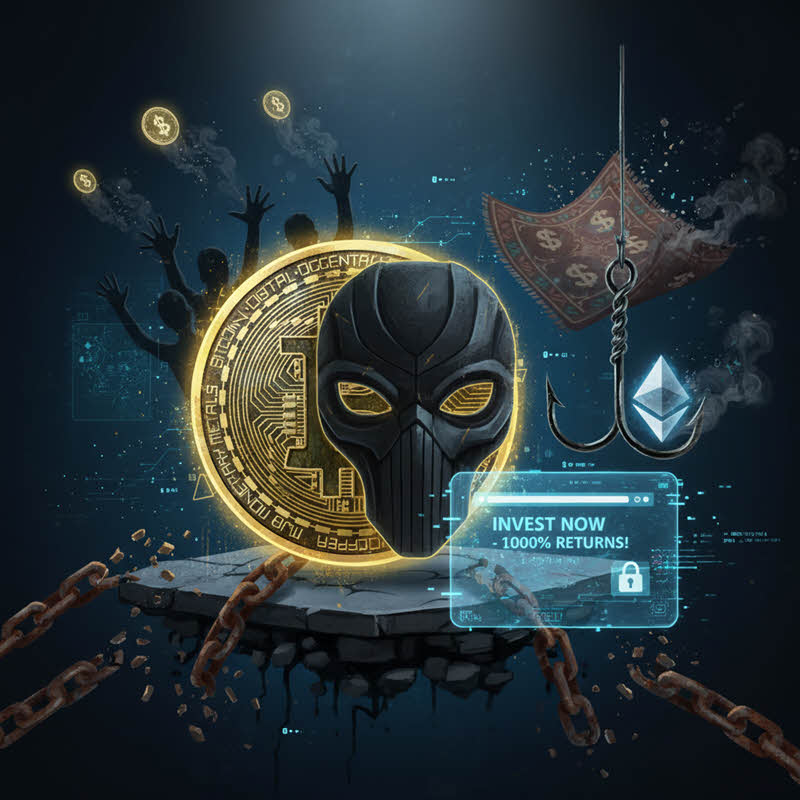

All the Most Common Types of Crypto Scams Worldwide – A Cautionary Lesson for Investors
Last updated: October 16, 2025 Read in fullscreen view
- 18 Oct 2020
 How to use the "Knowns" and "Unknowns" technique to manage assumptions 38/1089
How to use the "Knowns" and "Unknowns" technique to manage assumptions 38/1089 - 18 Oct 2024
 The Dark Side of Japan’s Work Culture 28/49
The Dark Side of Japan’s Work Culture 28/49 - 14 Aug 2024
 Blockchain Explained: Key Advantages and Limitations You Should Know 27/72
Blockchain Explained: Key Advantages and Limitations You Should Know 27/72 - 21 Nov 2025
 The Pressure of Short-Term Funding on Small-Budget IT Projects 25/35
The Pressure of Short-Term Funding on Small-Budget IT Projects 25/35 - 01 Oct 2020
 Fail fast, learn faster with Agile methodology 24/1047
Fail fast, learn faster with Agile methodology 24/1047 - 14 Oct 2021
 Advantages and Disadvantages of Time and Material Contract (T&M) 22/864
Advantages and Disadvantages of Time and Material Contract (T&M) 22/864 - 18 Dec 2025
 AI: Act Now or Wait Until You’re “Ready”? 22/42
AI: Act Now or Wait Until You’re “Ready”? 22/42 - 13 Dec 2020
 Move fast, fail fast, fail-safe 20/323
Move fast, fail fast, fail-safe 20/323 - 18 Aug 2022
 What are the consequences of poor requirements with software development projects? 20/274
What are the consequences of poor requirements with software development projects? 20/274 - 06 Feb 2021
 Why fail fast and learn fast? 19/450
Why fail fast and learn fast? 19/450 - 17 Mar 2025
 Integrating Salesforce with Yardi: A Guide to Achieving Success in Real Estate Business 19/202
Integrating Salesforce with Yardi: A Guide to Achieving Success in Real Estate Business 19/202 - 01 Mar 2023
 Bug Prioritization - What are the 5 levels of priority? 17/235
Bug Prioritization - What are the 5 levels of priority? 17/235 - 23 Sep 2021
 INFOGRAPHIC: Top 9 Software Outsourcing Mistakes 17/439
INFOGRAPHIC: Top 9 Software Outsourcing Mistakes 17/439 - 10 Nov 2022
 Poor Code Indicators and How to Improve Your Code? 16/231
Poor Code Indicators and How to Improve Your Code? 16/231 - 19 Oct 2021
 Is gold plating good or bad in project management? 15/816
Is gold plating good or bad in project management? 15/816 - 19 Apr 2021
 7 Most Common Time-Wasters For Software Development 14/556
7 Most Common Time-Wasters For Software Development 14/556 - 08 Oct 2022
 KPI - The New Leadership 12/602
KPI - The New Leadership 12/602 - 31 Oct 2021
 Tips to Fail Fast With Outsourcing 12/392
Tips to Fail Fast With Outsourcing 12/392 - 10 Dec 2023
 Pain points of User Acceptance Testing (UAT) 11/452
Pain points of User Acceptance Testing (UAT) 11/452 - 28 Dec 2021
 8 types of pricing models in software development outsourcing 10/437
8 types of pricing models in software development outsourcing 10/437 - 17 Feb 2022
 Prioritizing Software Requirements with Kano Analysis 10/304
Prioritizing Software Requirements with Kano Analysis 10/304 - 05 Jan 2024
 Easy ASANA tips & tricks for you and your team 9/200
Easy ASANA tips & tricks for you and your team 9/200 - 11 Jan 2024
 What are the Benefits and Limitations of Augmented Intelligence? 9/477
What are the Benefits and Limitations of Augmented Intelligence? 9/477 - 12 Mar 2024
 How do you create FOMO in software prospects? 9/167
How do you create FOMO in software prospects? 9/167 - 01 Jul 2025
 Southeast Asia Faces a Surge of “Fake AI Startups” 8/84
Southeast Asia Faces a Surge of “Fake AI Startups” 8/84 - 14 Mar 2024
 Why should you opt for software localization from a professional agency? 6/140
Why should you opt for software localization from a professional agency? 6/140 - 26 Dec 2023
 Improving Meeting Effectiveness Through the Six Thinking Hats 6/254
Improving Meeting Effectiveness Through the Six Thinking Hats 6/254 - 06 Nov 2019
 How to Access Software Project Size? 6/249
How to Access Software Project Size? 6/249
When Greed Wears the Mask of Technology
The explosive rise of cryptocurrency brought massive opportunities for quick wealth — but it also unleashed countless crypto scam types.
With little legal oversight, bad actors exploit blockchain technology to invent endless frauds — from fake crypto exchanges to sophisticated rug pulls.
This article helps you understand and learn how to spot a crypto scam before it’s too late.
The Most Common Types of Crypto Scams
Ponzi and Pyramid Schemes
Mechanism: Using funds from new investors to pay old ones, without any real product.
Signs: Promises of “guaranteed profit,” “passive income,” or “100% safe investment.”
Examples:
-
BitConnect (2016–2018) – One of the most infamous crypto scams, promising 1% daily returns before collapsing and wiping out over $3.5 billion.
-
PlusToken (China, 2019) – Over 3 million victims, with losses exceeding $2 billion.
Rug Pull
Mechanism: Developers create a token, pump the price, then drain the liquidity and disappear.
Example:
-
Squid Game Token (2021) – One of the most famous rug pulls, its price skyrocketed by 23 million percent before crashing to zero in minutes.
Signs:
-
No audit report
-
Shady tokenomics
-
Anonymous or hidden team
Pump and Dump
Mechanism: A group of influencers or traders creates hype to drive up prices, then dumps their holdings for profit.
Lesson: Don’t fall for last-minute “buy now before it’s too late” pitches — that’s a clear crypto scam warning.
Phishing and Fake Wallets/Websites
Mechanism: Hackers clone legitimate crypto wallet sites or apps (like MetaMask, TrustWallet, Binance) to steal credentials.
Example: Phishing crypto wallets — victims are tricked into entering their seed phrase on fake websites.
Signs:
-
Slightly misspelled URLs (e.g., binancee.com, metamask-login.io)
-
Identical design copied from the real website
Lesson: Never enter your private key or seed phrase anywhere unofficial.
Airdrop Scams
Mechanism: Scammers pretend to give free tokens to lure users into connecting their wallet or paying gas fees — then drain the funds.
Example: Airdrop scam warnings often spread on Telegram or Discord with fake “claim now” links.
Lesson: Free tokens can sometimes be the most expensive trap.
Romance Scams
Mechanism: Scammers build emotional relationships online, then persuade victims to invest in “safe crypto opportunities.”
Example: The pig butchering scam crypto — where victims are “fattened up” with trust before being completely drained.
Lesson: When someone says “invest for love,” it’s time to run.
Fake ICOs / IDOs
Mechanism: Fraudsters launch fake blockchain projects with convincing websites and whitepapers, then vanish.
Example: Centra Tech (2018) – Heavily promoted and celebrity-endorsed, yet its founders ended up with 8-year prison sentences.
Tip: To learn how to spot a crypto scam, always check the audit, team credentials, and legal registrations.
Malware and Keyloggers
Mechanism: Fake “crypto analysis tools” or “free wallets” secretly install malware to steal data and assets.
Lesson: Never download wallets or trading tools from unknown links. Use cold wallets for large holdings.
NFT Scams
Mechanism: Fake NFT projects inflate prices, sell out, then vanish — or use stolen artwork.
Example: Evolved Apes – Sold 10,000 NFTs, with the founder running off with $2.7 million.
Lesson: NFTs can be another form of crypto scam if you skip due diligence.
Exchange Scams
Mechanism: Fake crypto exchanges simulate high trading volumes, freeze user accounts, or disappear with funds.
Example: Mt. Gox – Once handled 70% of all BTC transactions before collapsing after losing 850,000 BTC.
Lesson: Only use verified and globally reputable exchanges.
Survival Lessons for Crypto Investors
-
Trust data, not promises.
If a project guarantees fixed profits or total safety — consider it a crypto scam warning. -
Check audits and team transparency.
Google: [Project name] + “scam” or [Project name] + “audit report” — a quick way to filter frauds. -
Keep your own wallet — not your coins on exchanges.
“Not your keys, not your coins” — the golden rule to avoid phishing crypto wallets. -
Don’t invest because of FOMO.
The fear of missing out is exactly what scammers exploit. -
Think like a hacker.
Before trusting anyone, ask yourself: If I were the scammer, how would I exploit my own weakness?
Final Thought: Don’t Let Curiosity Become the Price You Pay
Blockchain technology doesn’t scam you — people do, through blockchain.
In a world where a single click can erase everything, knowledge and skepticism are your final layers of protection.
Smart investing isn’t about finding the next coin to moon — it’s about staying far away from the crypto scams flooding the digital frontier.






























 Link copied!
Link copied!
 Recently Updated News
Recently Updated News