Harnessing the Power of Ekiden Methodology Across Multiple Domains
Last updated: October 20, 2025 Read in fullscreen view
- 01 Aug 2024
 The Standish Group report 83.9% of IT projects partially or completely fail 339/2058
The Standish Group report 83.9% of IT projects partially or completely fail 339/2058 - 02 Nov 2023
 Unlocking Success with The Amoeba Management Model: Key Lessons, Pros & Cons, and Finding the Perfect Fit 275/889
Unlocking Success with The Amoeba Management Model: Key Lessons, Pros & Cons, and Finding the Perfect Fit 275/889 - 10 Nov 2021
 5S methodology - the SECRET to Japanese SUCCESS 160/1833
5S methodology - the SECRET to Japanese SUCCESS 160/1833 - 09 Sep 2022
 Kaizen, Kaikaku and Kakushin – what’s the difference? 156/3081
Kaizen, Kaikaku and Kakushin – what’s the difference? 156/3081 - 24 Nov 2022
 Genba Genbutsu Genjitsu (3Gs), (Go to the Genba & see for yourself!) 136/3059
Genba Genbutsu Genjitsu (3Gs), (Go to the Genba & see for yourself!) 136/3059 - 01 Dec 2023
 What is Amoeba Management? 108/1043
What is Amoeba Management? 108/1043 - 13 Apr 2024
 Lessons on Teamwork and Leadership from Chinese story book "Journey to the West" 81/1084
Lessons on Teamwork and Leadership from Chinese story book "Journey to the West" 81/1084 - 01 Apr 2022
 Ishikawa (fishbone) diagram in software project management 56/3145
Ishikawa (fishbone) diagram in software project management 56/3145 - 02 Nov 2021
 What is Terms of Reference (ToR)? 46/1564
What is Terms of Reference (ToR)? 46/1564 - 18 Oct 2020
 How to use the "Knowns" and "Unknowns" technique to manage assumptions 38/1089
How to use the "Knowns" and "Unknowns" technique to manage assumptions 38/1089 - 17 Mar 2023
 Reduce waste in software development with 3M model: Muda, Mura, Muri 36/960
Reduce waste in software development with 3M model: Muda, Mura, Muri 36/960 - 13 Oct 2025
 Mastering the Dynamic Squad Model: A Modern Approach to Agile Teams 35/179
Mastering the Dynamic Squad Model: A Modern Approach to Agile Teams 35/179 - 09 Sep 2022
 What is 5 Whys (Five Whys)? 34/971
What is 5 Whys (Five Whys)? 34/971 - 12 Dec 2024
 Danshari: A Japanese Minimalist Philosophy for Cleaner Code and Leaner IT Operations 33/97
Danshari: A Japanese Minimalist Philosophy for Cleaner Code and Leaner IT Operations 33/97 - 29 Jan 2026
 Honne and Tatemae: Why Do Japanese People Seem Excessively Polite and Indirect? 31/40
Honne and Tatemae: Why Do Japanese People Seem Excessively Polite and Indirect? 31/40 - 27 Aug 2022
 Kaizen - Culture of Continuous Improvement and Lean Thinking 29/825
Kaizen - Culture of Continuous Improvement and Lean Thinking 29/825 - 29 Aug 2022
 Difference between Kaizen and Innovation 29/911
Difference between Kaizen and Innovation 29/911 - 03 Jan 2024
 What is the Ringi process? 29/974
What is the Ringi process? 29/974 - 04 Mar 2024
 Tree Ring Management: Take the Long Term View and Grow Your Business Slowly 29/444
Tree Ring Management: Take the Long Term View and Grow Your Business Slowly 29/444 - 03 Apr 2022
 Microsoft Solutions Framework (MSF) 29/1273
Microsoft Solutions Framework (MSF) 29/1273 - 01 Mar 2022
 The Toyota Way Management Principles 28/784
The Toyota Way Management Principles 28/784 - 01 Oct 2020
 Fail fast, learn faster with Agile methodology 24/1047
Fail fast, learn faster with Agile methodology 24/1047 - 14 Oct 2021
 Advantages and Disadvantages of Time and Material Contract (T&M) 22/864
Advantages and Disadvantages of Time and Material Contract (T&M) 22/864 - 02 Feb 2022
 Yokoten: Best Practice Sharing from a success 22/1374
Yokoten: Best Practice Sharing from a success 22/1374 - 13 Jul 2022
 Applying the business mantra "HORENSO" to Achieve 360-degree Communication 22/921
Applying the business mantra "HORENSO" to Achieve 360-degree Communication 22/921 - 15 Apr 2022
 Total Quality Management (TQM) - Japanese-style management approach to quality improvement. 22/695
Total Quality Management (TQM) - Japanese-style management approach to quality improvement. 22/695 - 07 Mar 2023
 Japan’s Unusual Farming Strategy: Renting Land and Leaving It Fallow for 5 Years — Here’s the Truth… 21/80
Japan’s Unusual Farming Strategy: Renting Land and Leaving It Fallow for 5 Years — Here’s the Truth… 21/80 - 18 Aug 2022
 What are the consequences of poor requirements with software development projects? 20/274
What are the consequences of poor requirements with software development projects? 20/274 - 13 Dec 2020
 Move fast, fail fast, fail-safe 20/323
Move fast, fail fast, fail-safe 20/323 - 06 Feb 2021
 Why fail fast and learn fast? 19/450
Why fail fast and learn fast? 19/450 - 15 Jul 2022
 Hansei Methodology: Continuously Engaging People in Improvement 18/707
Hansei Methodology: Continuously Engaging People in Improvement 18/707 - 31 Dec 2025
 26 Things You Should Do Now to Prepare for 2026 18/34
26 Things You Should Do Now to Prepare for 2026 18/34 - 23 Sep 2021
 INFOGRAPHIC: Top 9 Software Outsourcing Mistakes 17/439
INFOGRAPHIC: Top 9 Software Outsourcing Mistakes 17/439 - 01 Mar 2023
 Bug Prioritization - What are the 5 levels of priority? 17/235
Bug Prioritization - What are the 5 levels of priority? 17/235 - 18 Dec 2023
 The Cone of Uncertainty in Scrum & Requirement Definition 17/701
The Cone of Uncertainty in Scrum & Requirement Definition 17/701 - 10 Nov 2022
 Poor Code Indicators and How to Improve Your Code? 16/231
Poor Code Indicators and How to Improve Your Code? 16/231 - 19 Oct 2021
 Is gold plating good or bad in project management? 15/816
Is gold plating good or bad in project management? 15/816 - 12 Aug 2022
 What is End-to-end project management? 15/444
What is End-to-end project management? 15/444 - 19 Apr 2021
 7 Most Common Time-Wasters For Software Development 14/556
7 Most Common Time-Wasters For Software Development 14/556 - 26 Sep 2024
 Successful Project Management Techniques You Need to Look Out For 14/401
Successful Project Management Techniques You Need to Look Out For 14/401 - 10 Apr 2024
 The Parking Lot Method: Unlocking a Simple Secret to Supercharge Your Productivity 14/481
The Parking Lot Method: Unlocking a Simple Secret to Supercharge Your Productivity 14/481 - 18 Oct 2021
 Key Elements to Ramping Up a Large Team 13/1198
Key Elements to Ramping Up a Large Team 13/1198 - 06 Jun 2022
 HEIJUNKA: The art of leveling production 13/552
HEIJUNKA: The art of leveling production 13/552 - 05 Jun 2023
 Fractional, Part-Time (virtual) or Interim CTO: Who Will Cover Your Business Needs? 13/147
Fractional, Part-Time (virtual) or Interim CTO: Who Will Cover Your Business Needs? 13/147 - 19 Sep 2022
 Jidoka in Software Development and Odoo ERP/MRP 12/527
Jidoka in Software Development and Odoo ERP/MRP 12/527 - 07 Jul 2022
 Managing Project Execution Terms 12/411
Managing Project Execution Terms 12/411 - 31 Oct 2021
 Tips to Fail Fast With Outsourcing 12/392
Tips to Fail Fast With Outsourcing 12/392 - 08 Oct 2022
 KPI - The New Leadership 12/602
KPI - The New Leadership 12/602 - 01 Jan 2024
 6 Japanese Life Principles That Quietly Transform You 12/101
6 Japanese Life Principles That Quietly Transform You 12/101 - 23 Jun 2024
 Best Practices for Managing Project Escalations 11/207
Best Practices for Managing Project Escalations 11/207 - 10 Dec 2023
 Pain points of User Acceptance Testing (UAT) 11/452
Pain points of User Acceptance Testing (UAT) 11/452 - 01 Jan 2023
 How To Use Poka-Yoke (Mistake Proofing) Technique To Improve Software Quality 10/647
How To Use Poka-Yoke (Mistake Proofing) Technique To Improve Software Quality 10/647 - 12 Mar 2022
 The u-Japan concept 10/296
The u-Japan concept 10/296 - 06 Jun 2022
 Change Management at the Project Level 10/309
Change Management at the Project Level 10/309 - 02 May 2022
 What Is RAID in Project Management? (With Pros and Cons) 10/813
What Is RAID in Project Management? (With Pros and Cons) 10/813 - 13 Jan 2020
 Quiz: Test your understanding project cost management 10/609
Quiz: Test your understanding project cost management 10/609 - 28 Dec 2021
 8 types of pricing models in software development outsourcing 10/437
8 types of pricing models in software development outsourcing 10/437 - 17 Feb 2022
 Prioritizing Software Requirements with Kano Analysis 10/304
Prioritizing Software Requirements with Kano Analysis 10/304 - 20 Jul 2022
 Software Myths and Realities 10/891
Software Myths and Realities 10/891 - 14 Jun 2022
 Example and Excel template of a RACI chart in Software Development 10/804
Example and Excel template of a RACI chart in Software Development 10/804 - 22 May 2022
 What are common mistakes that new or inexperienced managers make? 9/286
What are common mistakes that new or inexperienced managers make? 9/286 - 02 Nov 2022
 Difference between Change Management and Project Management 9/232
Difference between Change Management and Project Management 9/232 - 24 Nov 2023
 The project management paradox: Achieving MORE by doing LESS 9/218
The project management paradox: Achieving MORE by doing LESS 9/218 - 11 Jan 2024
 What are the Benefits and Limitations of Augmented Intelligence? 9/477
What are the Benefits and Limitations of Augmented Intelligence? 9/477 - 12 Mar 2024
 How do you create FOMO in software prospects? 9/167
How do you create FOMO in software prospects? 9/167 - 05 Jan 2024
 Easy ASANA tips & tricks for you and your team 9/200
Easy ASANA tips & tricks for you and your team 9/200 - 07 Dec 2023
 12 project management myths to avoid 8/189
12 project management myths to avoid 8/189 - 09 May 2022
 Build one to throw away vs Second-system effect: What are differences? 8/316
Build one to throw away vs Second-system effect: What are differences? 8/316 - 02 Dec 2021
 3 Ways to Avoid Scope Creep in IT Consulting 8/206
3 Ways to Avoid Scope Creep in IT Consulting 8/206 - 27 Jan 2020
 Should a project manager push developers to work more hours due to mistakes of manager schedule setting? 8/434
Should a project manager push developers to work more hours due to mistakes of manager schedule setting? 8/434 - 15 May 2022
 20 Common Mistakes Made by New or Inexperienced Project Managers 7/280
20 Common Mistakes Made by New or Inexperienced Project Managers 7/280 - 01 Jun 2020
 Japan Business Review (JBR) 7/330
Japan Business Review (JBR) 7/330 - 17 Oct 2021
 Does Fast Tracking increase project cost? 6/368
Does Fast Tracking increase project cost? 6/368 - 06 Nov 2019
 How to Access Software Project Size? 6/249
How to Access Software Project Size? 6/249 - 10 May 2022
 Levels of Teamwork 6/197
Levels of Teamwork 6/197 - 03 Jan 2023
 Organizing your agile teams? Think about M.A.T (Mastery, Autonomy, Purpose) 6/375
Organizing your agile teams? Think about M.A.T (Mastery, Autonomy, Purpose) 6/375 - 14 Mar 2024
 Why should you opt for software localization from a professional agency? 6/140
Why should you opt for software localization from a professional agency? 6/140 - 26 Dec 2023
 Improving Meeting Effectiveness Through the Six Thinking Hats 6/254
Improving Meeting Effectiveness Through the Six Thinking Hats 6/254 - 01 Mar 2024
 10 Project Management Myths 5/143
10 Project Management Myths 5/143 - 30 Nov 2023
 Project Managers, Focus on Outcomes — Not Deliverables 5/159
Project Managers, Focus on Outcomes — Not Deliverables 5/159 - 26 Nov 2024
 Harnessing Time Management Skills for Remote Team Effectiveness 4/203
Harnessing Time Management Skills for Remote Team Effectiveness 4/203 - 02 Jun 2024
 Reviving Ancient Wisdom: The Spiritual Side of Project Management 3/233
Reviving Ancient Wisdom: The Spiritual Side of Project Management 3/233 - 01 Aug 2022
 Is planning "set it and forget it" or "set it and check it"? 3/277
Is planning "set it and forget it" or "set it and check it"? 3/277 - 21 Jun 2024
 Dead Horses and the Escalation of Commitment 2/138
Dead Horses and the Escalation of Commitment 2/138 - 18 Feb 2026
 "Hit and Run" Project Management: Balancing Speed with Sustainability 2/7
"Hit and Run" Project Management: Balancing Speed with Sustainability 2/7
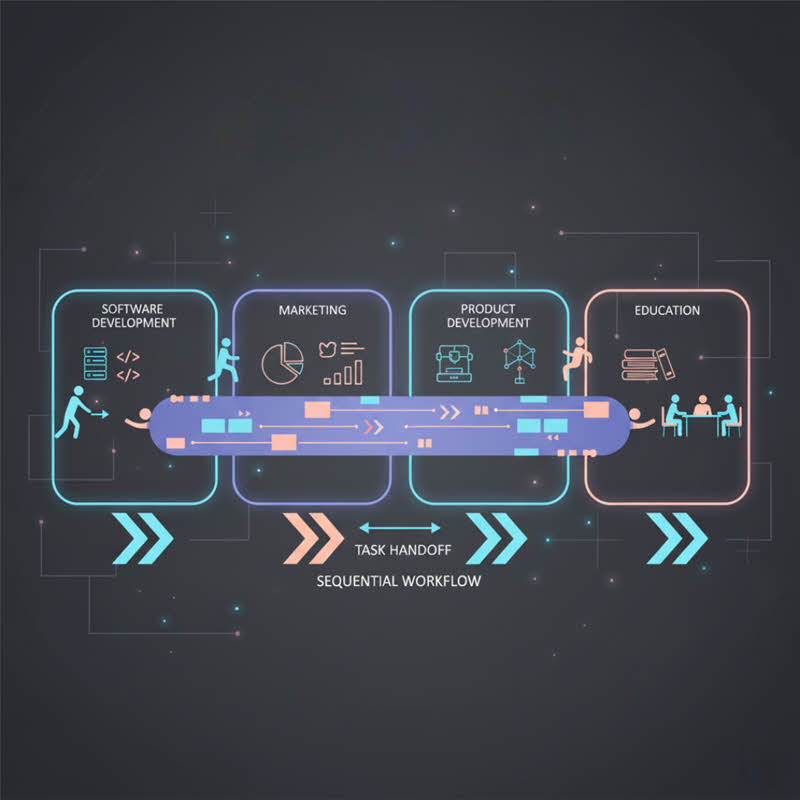
The Ekiden methodology draws inspiration from Japan’s long-distance relay races, where teams pass a tasuki sash to maintain momentum, and from the Ekiden blockchain platform, which runs confidential off-chain smart contracts. Both emphasize sequential handoffs, teamwork, and efficiency.
In business and technology, Ekiden enhances agile workflows by ensuring tasks move smoothly from one team member to another. In software development, squads can pick up sprints from previous stages, while marketing teams can relay campaigns from creative design to analytics. Product development, healthcare, and education also benefit from structured, iterative collaboration.
Adopting Ekiden methodology leads to enhanced accountability, reduced bottlenecks, and scalable collaboration, transforming how teams operate in modern organizations.
In today’s fast-paced business environment, agility, collaboration, and efficiency are more than just buzzwords—they are critical success factors. One approach that has been gaining traction among project managers, product teams, and operational leaders is the Ekiden methodology. Rooted in principles of sequential teamwork and iterative delivery, Ekiden provides a framework that enhances productivity and adaptability in various contexts.
What is Ekiden Methodology?
Inspired by the Japanese long-distance relay race, Ekiden methodology emphasizes relay-style collaboration within teams. Instead of working in isolated silos or strictly linear processes, teams pass responsibilities smoothly from one member or squad to another, ensuring continuity, accountability, and consistent momentum. Each “leg” of the project builds on the previous one, with clear checkpoints, handoffs, and shared objectives.
The term "Ekiden methodology" can refer to two different concepts:
- A Japanese long-distance relay running race
- A blockchain platform for confidential, off-chain smart contract execution
Ekiden as a Running Race
- Definition: A type of long-distance relay race, particularly popular in Japan.
- Teamwork: Teams of runners cover consecutive legs of a race.
- The Tasuki: The defining feature is the passing of a sash called a tasuki, symbolizing teamwork and continuity.
- History: The name "ekiden" means "station message," originating from a historical system of passing messages along postal routes.
The race emphasizes relay-style collaboration, where each runner contributes to the collective goal, creating momentum and accountability. This concept directly inspired the Ekiden methodology in business and technology, emphasizing sequential handoffs, clear responsibilities, and iterative progress.
Ekiden as a Blockchain Platform
- Definition: A platform for running smart contracts off-chain while maintaining privacy and security.
- Architecture: It separates computation from blockchain consensus, with smart contract computations happening off-chain in secure environments.
- Technology: Uses Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs) to ensure confidentiality and integrity for private data and computations.
- Benefits: Provides high performance, low cost, and privacy protection compared to on-chain execution.
- Implementation: Can be built on top of various blockchains and supports contract development in languages like Rust and the EVM.
This blockchain-based approach extends the relay principle to computation, passing tasks securely through multiple stages while maintaining trust, privacy, and efficiency.
Key characteristics of Ekiden methodology include:
- Sequential collaboration with parallel efficiency: Tasks move forward without bottlenecks.
- Transparent handoffs: Every team member knows what has been done and what is next.
- Iterative progress with feedback loops: Continuous improvements at each stage.
- Cross-functional integration: Encourages diverse expertise to contribute at appropriate stages.
Applications of Ekiden Methodology in Business
1. Software Development and IT Projects
Ekiden methodology is naturally suited for software development, where modularity and iterative delivery are essential.
- Agile-friendly integration: Teams can implement sprints in a relay fashion, where each squad or developer picks up work from the previous stage.
- Quality assurance handoff: Continuous integration and testing can follow the relay principle, reducing bugs and improving release cycles.
- Cross-functional squads: Developers, testers, UX designers, and DevOps engineers can collaborate sequentially while maintaining overall velocity.
2. Marketing and Content Production
Marketing campaigns often involve multiple departments: creative, strategy, analytics, and operations. Ekiden methodology ensures smooth coordination:
- Campaign relay: Creative content moves seamlessly from design to copywriting, review, and distribution.
- Analytics feedback loops: Performance insights feed back into the next campaign phase, enhancing adaptability.
- Multi-channel alignment: Teams working on social media, email marketing, and PR can integrate efficiently without duplication of effort.
3. Product Development and Manufacturing
From concept to market-ready products, the Ekiden approach provides structure and clarity:
- Sequential prototyping: Design, engineering, and testing phases can be clearly segmented yet interconnected.
- Supply chain coordination: Handoffs between suppliers, manufacturers, and logistics teams are optimized for timing and accountability.
- Continuous improvement: Feedback at each stage informs iterative product enhancements.
4. Healthcare and Research
Healthcare projects—clinical trials, hospital operations, and research studies—benefit from a structured relay approach:
- Patient care coordination: Medical teams can ensure each phase of treatment is delivered efficiently.
- Research collaboration: Data collection, analysis, and reporting can follow a clear, relay-style workflow, reducing errors and delays.
- Policy implementation: Public health initiatives can be rolled out in stages with clear responsibilities.
5. Education and Training Programs
Ekiden methodology enhances collaborative learning and program delivery:
- Curriculum development: Subject matter experts can pass modules to instructional designers and educators efficiently.
- Project-based learning: Students work in teams, handing off deliverables and learning from each stage.
- Continuous assessment: Feedback loops allow instructors to refine the learning path progressively.
Why Organizations Should Consider Ekiden
Implementing Ekiden methodology offers several benefits:
- Enhanced accountability: Each team member knows their role and contribution.
- Reduced bottlenecks: Sequential handoffs prevent delays and duplicated effort.
- Scalable collaboration: Works for small teams or large enterprises.
- Resilient workflows: Iterative feedback allows for continuous improvement and adaptability.
In conclusion, Ekiden methodology is more than just a project management style; it is a philosophy of teamwork, continuity, and efficiency. Whether in software development, marketing, product design, healthcare, or education, adopting a relay-style workflow can transform how teams operate, boosting productivity, accountability, and overall success.





























 Link copied!
Link copied!
 Recently Updated News
Recently Updated News