Poor requirements: Poor inputs result in poor outputs
Last updated: July 08, 2024 Read in fullscreen view
- 15 Feb 2024
 What is a Cut-Over in Software Development? 69/1320
What is a Cut-Over in Software Development? 69/1320 - 02 Nov 2023
 Differences between software walkthrough, review, and inspection 54/2112
Differences between software walkthrough, review, and inspection 54/2112 - 28 Oct 2023
 The GOLDEN Rules of Software Engineering 47/593
The GOLDEN Rules of Software Engineering 47/593 - 13 Oct 2021
 Outsourcing Software Development: MVP, Proof of Concept (POC) and Prototyping. Which is better? 40/486
Outsourcing Software Development: MVP, Proof of Concept (POC) and Prototyping. Which is better? 40/486 - 18 Oct 2020
 How to use the "Knowns" and "Unknowns" technique to manage assumptions 38/1089
How to use the "Knowns" and "Unknowns" technique to manage assumptions 38/1089 - 12 Oct 2022
 14 Common Reasons Software Projects Fail (And How To Avoid Them) 32/568
14 Common Reasons Software Projects Fail (And How To Avoid Them) 32/568 - 14 Oct 2021
 Stream Story - Low land stream or fast moving stream? 31/634
Stream Story - Low land stream or fast moving stream? 31/634 - 19 Oct 2021
 Software development life cycles 30/702
Software development life cycles 30/702 - 13 Oct 2021
 What is Bug Convergence? Why is it important for User Acceptance Testing (UAT)? 28/759
What is Bug Convergence? Why is it important for User Acceptance Testing (UAT)? 28/759 - 08 Dec 2021
 What Are The 4 Types of Maintenance Strategies? 25/1146
What Are The 4 Types of Maintenance Strategies? 25/1146 - 05 May 2021
 TIGO Magic Scale - PoC tool for you to apply dichotomous thinking before submitting RFP 25/344
TIGO Magic Scale - PoC tool for you to apply dichotomous thinking before submitting RFP 25/344 - 01 Oct 2020
 Fail fast, learn faster with Agile methodology 24/1047
Fail fast, learn faster with Agile methodology 24/1047 - 14 Oct 2021
 Advantages and Disadvantages of Time and Material Contract (T&M) 22/864
Advantages and Disadvantages of Time and Material Contract (T&M) 22/864 - 13 May 2022
 IT Training and Development: The most effective options for upskilling IT staff 21/1146
IT Training and Development: The most effective options for upskilling IT staff 21/1146 - 02 Dec 2022
 3 Levels of Quality in KANO Analysis Model 21/1120
3 Levels of Quality in KANO Analysis Model 21/1120 - 18 Aug 2022
 What are the consequences of poor requirements with software development projects? 20/274
What are the consequences of poor requirements with software development projects? 20/274 - 13 Dec 2020
 Move fast, fail fast, fail-safe 20/323
Move fast, fail fast, fail-safe 20/323 - 06 Feb 2021
 Why fail fast and learn fast? 20/451
Why fail fast and learn fast? 20/451 - 23 Sep 2021
 INFOGRAPHIC: Top 9 Software Outsourcing Mistakes 17/439
INFOGRAPHIC: Top 9 Software Outsourcing Mistakes 17/439 - 04 Oct 2021
 Product Validation: The Key to Developing the Best Product Possible 17/320
Product Validation: The Key to Developing the Best Product Possible 17/320 - 01 Mar 2023
 Bug Prioritization - What are the 5 levels of priority? 17/235
Bug Prioritization - What are the 5 levels of priority? 17/235 - 05 Sep 2023
 The Cold Start Problem: How to Start and Scale Network Effects 17/203
The Cold Start Problem: How to Start and Scale Network Effects 17/203 - 07 Oct 2025
 Case Study: Using the “Messaging House” Framework to Build a Digital Transformation Roadmap 17/86
Case Study: Using the “Messaging House” Framework to Build a Digital Transformation Roadmap 17/86 - 01 Feb 2024
 How long does it take to develop software? 16/224
How long does it take to develop software? 16/224 - 11 Oct 2021
 10 Myths About Low-End Project Management Software 16/340
10 Myths About Low-End Project Management Software 16/340 - 05 Mar 2021
 How do you minimize risks when you outsource software development? 16/336
How do you minimize risks when you outsource software development? 16/336 - 31 Aug 2022
 What are the best practices for software contract negotiations? 16/260
What are the best practices for software contract negotiations? 16/260 - 10 Nov 2022
 Poor Code Indicators and How to Improve Your Code? 16/231
Poor Code Indicators and How to Improve Your Code? 16/231 - 19 Oct 2021
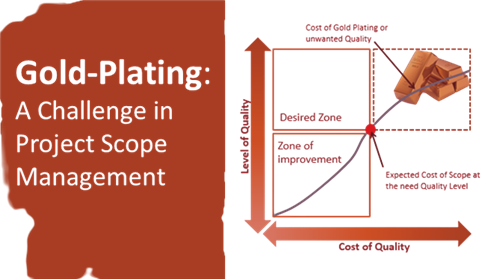
 Is gold plating good or bad in project management? 15/816
Is gold plating good or bad in project management? 15/816 - 19 Apr 2021
 7 Most Common Time-Wasters For Software Development 14/556
7 Most Common Time-Wasters For Software Development 14/556 - 28 Jul 2022
 POC, Prototypes, Pilots and MVP: What Are the Differences? 13/697
POC, Prototypes, Pilots and MVP: What Are the Differences? 13/697 - 28 Oct 2022
 Build Operate Transfer (B.O.T) Model in Software Outsourcing 12/406
Build Operate Transfer (B.O.T) Model in Software Outsourcing 12/406 - 31 Oct 2021
 Tips to Fail Fast With Outsourcing 12/392
Tips to Fail Fast With Outsourcing 12/392 - 08 Oct 2022
 KPI - The New Leadership 12/603
KPI - The New Leadership 12/603 - 12 Dec 2021
 Zero Sum Games Agile vs. Waterfall Project Management Methods 11/410
Zero Sum Games Agile vs. Waterfall Project Management Methods 11/410 - 04 Oct 2022
 Which ERP implementation strategy is right for your business? 11/313
Which ERP implementation strategy is right for your business? 11/313 - 10 Dec 2023
 Pain points of User Acceptance Testing (UAT) 11/452
Pain points of User Acceptance Testing (UAT) 11/452 - 02 May 2022
 What Is RAID in Project Management? (With Pros and Cons) 10/813
What Is RAID in Project Management? (With Pros and Cons) 10/813 - 05 Jan 2024
 Easy ASANA tips & tricks for you and your team 10/201
Easy ASANA tips & tricks for you and your team 10/201 - 11 Jan 2024
 What are the Benefits and Limitations of Augmented Intelligence? 10/478
What are the Benefits and Limitations of Augmented Intelligence? 10/478 - 17 Feb 2022
 Prioritizing Software Requirements with Kano Analysis 10/304
Prioritizing Software Requirements with Kano Analysis 10/304 - 28 Dec 2021
 8 types of pricing models in software development outsourcing 10/437
8 types of pricing models in software development outsourcing 10/437 - 18 Jul 2021
 How To Ramp Up An Offshore Software Development Team Quickly 9/593
How To Ramp Up An Offshore Software Development Team Quickly 9/593 - 12 Mar 2024
 How do you create FOMO in software prospects? 9/167
How do you create FOMO in software prospects? 9/167 - 06 Mar 2024
 [SemRush] What Are LSI Keywords & Why They Don‘t Matter 7/176
[SemRush] What Are LSI Keywords & Why They Don‘t Matter 7/176 - 21 Oct 2025
 Cloud-Native Development: Why It’s the Future of Enterprise IT 7/80
Cloud-Native Development: Why It’s the Future of Enterprise IT 7/80 - 01 Oct 2020
 Handling tight project deadlines as a business analyst 7/331
Handling tight project deadlines as a business analyst 7/331 - 03 Nov 2022
 Questions and answers about Kano Model 7/864
Questions and answers about Kano Model 7/864 - 06 Nov 2019
 How to Access Software Project Size? 6/249
How to Access Software Project Size? 6/249 - 12 Aug 2024
 Understanding Google Analytics in Mumbai: A Beginner's Guide 6/99
Understanding Google Analytics in Mumbai: A Beginner's Guide 6/99 - 14 Mar 2024
 Why should you opt for software localization from a professional agency? 6/140
Why should you opt for software localization from a professional agency? 6/140 - 26 Dec 2023
 Improving Meeting Effectiveness Through the Six Thinking Hats 6/254
Improving Meeting Effectiveness Through the Six Thinking Hats 6/254 - 01 Dec 2023
 Laws of Project Management 5/302
Laws of Project Management 5/302 - 01 May 2024
 Warren Buffett’s Golden Rule for Digital Transformation: Avoiding Tech Overload 3/205
Warren Buffett’s Golden Rule for Digital Transformation: Avoiding Tech Overload 3/205
Garbage in, garbage out: poor inputs result in poor outputs
“Garbage In, Garbage Out” (GIGO) is a concept in information technology and computer science that emphasizes the importance of input quality. It implies that if the data input into a system is flawed or inaccurate, the resulting output will also be flawed or inaccurate.
Poor definition of software requirements can lead to failure of software development projects
Software development requirements are pivotal and central to every successful software development project. Poor requirements practices alone can doom any application development process. No matter how well designed and constructed or well tested an application might be, it is essentially useless if it fails to meet the business needs.
Defects in software development requirements are the sources of the majority of defects that are identified during testing and problems with requirements are among the top causes of project failure.
Common software development requirements problems include incomplete or inaccurate requirements, poorly managed requirements change and missed requirements. The first step of requirements management is accurately capturing the requirements and defining it. Confusion about what is required pretty much guarantees the requirements will not be met and increases the chance of product failure.
The inability to identify all the impacts and notify anyone impacted by a change leads to poor change management. A poorly executed change means wasted efforts, outdated information and design conflict. This drives up cost and creates project delay.
Significant documentation is required of companies who must comply with regulations or meet standards. Those that lack requirements traceability must invest significant time preparing records to prove compliance. Those that have traceability have a far easier time producing reports and records that support compliance as they can automatically trace the regulatory down to the details proving it was satisfied.
Software requirements sit in a tricky zone between business and technical thinking
Depending on who writes them they can fall too far toward one camp or the other. A technically written set of requirements may concentrate too much on implementation issues, e.g. data design, and miss out on the actual benefits the business was after. Conversely, specifications written by non-technical people can be wordy, ambiguous, and repetitive.
FAQ
What are the effects of poor software requirements?
Poor software requirements can create further technical problems resulting in poor customer responsiveness, long delivery times, late deliveries, defects, rising develoment costs, and poor performing teams.
What is the negative consequences of poor requirements?
Here are some of how bad the quality of requirements can lead to project failure. It is easy to lose track of the specific goals of a project if the goals are not documented properly. It means that because the scope of a project is not defined in detail, unnecessary or misguided work starts to take place.
Is it possible to develop a software with incomplete requirements?
It’s always possible to develop incomplete software from incomplete requirements, you develop what you can, based on what you know. Requirements, BTW, are never complete, we do the best we can. What is more concerning than incomplete requirements are incorrect requirements, poorly written requirements, and changing requirements. These can and do dramatically increase the development cost of a project, oftentimes to the point where the project fails. Managing requirements is the most critical and most often under-funded activity in any software project.
What are the risks associated with software requirements specification?
Some of the requirement risks are Poor definition of requirements, Inadequate of requirements, Lack of testing, poor definition of requirements etc.









04102024050214_thumb.jpg)





















 Link copied!
Link copied!
 Recently Updated News
Recently Updated News