Artificial Intelligence vs. Machine Learning: A Deep Dive into Their Applications and Use Cases
Last updated: October 18, 2025 Read in fullscreen view
- 05 Oct 2025
 The New Facebook Algorithm: A Paradigm Shift in Content Discovery 66/109
The New Facebook Algorithm: A Paradigm Shift in Content Discovery 66/109 - 12 Dec 2025
 FlexClip AI Video Magic Review: Professional AI-Powered Video Editing 62/97
FlexClip AI Video Magic Review: Professional AI-Powered Video Editing 62/97 - 06 Dec 2025
 Enterprise Operations 2.0: Why AI Agents Are Replacing Traditional Automation 48/83
Enterprise Operations 2.0: Why AI Agents Are Replacing Traditional Automation 48/83 - 23 Dec 2025
 Microsoft Power Automate vs. n8n: What’s the Real Difference? 47/77
Microsoft Power Automate vs. n8n: What’s the Real Difference? 47/77 - 25 Nov 2025
 How AI Agents Are Redefining Enterprise Automation and Decision-Making 46/96
How AI Agents Are Redefining Enterprise Automation and Decision-Making 46/96 - 20 Jan 2022
 Difference between Bug, Defect, Error, Fault & Failure 46/1334
Difference between Bug, Defect, Error, Fault & Failure 46/1334 - 17 Oct 2022
 What is the difference between low-end, mid-end and high-end solutions of project management software? 42/1465
What is the difference between low-end, mid-end and high-end solutions of project management software? 42/1465 - 17 Jul 2023
 What Is SSL? A Simple Explanation Even a 10-Year-Old Can Understand 42/120
What Is SSL? A Simple Explanation Even a 10-Year-Old Can Understand 42/120 - 06 Nov 2025
 Top 10 AI Development Companies in the USA to Watch in 2026 41/90
Top 10 AI Development Companies in the USA to Watch in 2026 41/90 - 13 Oct 2021
 Outsourcing Software Development: MVP, Proof of Concept (POC) and Prototyping. Which is better? 40/486
Outsourcing Software Development: MVP, Proof of Concept (POC) and Prototyping. Which is better? 40/486 - 05 Jul 2020
 What is Sustaining Software Engineering? 38/1301
What is Sustaining Software Engineering? 38/1301 - 07 Dec 2021
 What's the difference between soft freeze, hard freeze and customization freeze? 38/1256
What's the difference between soft freeze, hard freeze and customization freeze? 38/1256 - 01 Jul 2025
 The Hidden Costs of Not Adopting AI Agents: Risk of Falling Behind 38/164
The Hidden Costs of Not Adopting AI Agents: Risk of Falling Behind 38/164 - 02 Dec 2025
 The Question That Shook Asia: What Happens When We Ask AI to Choose Between a Mother and a Wife? 37/63
The Question That Shook Asia: What Happens When We Ask AI to Choose Between a Mother and a Wife? 37/63 - 03 Oct 2025
 Top CMS Trends 2026: The Future of Digital Content Management 37/55
Top CMS Trends 2026: The Future of Digital Content Management 37/55 - 03 Aug 2022
 What Are OLAs? SLAs vs OLAs vs UCs: What’s The Difference? 36/1064
What Are OLAs? SLAs vs OLAs vs UCs: What’s The Difference? 36/1064 - 20 Dec 2025
 The Future of IT Consulting: Key Trends for 2026–2030 35/67
The Future of IT Consulting: Key Trends for 2026–2030 35/67 - 22 Dec 2025
 The Role of Automotive Software in Building Smarter Vehicles 35/59
The Role of Automotive Software in Building Smarter Vehicles 35/59 - 12 Oct 2022
 14 Common Reasons Software Projects Fail (And How To Avoid Them) 32/568
14 Common Reasons Software Projects Fail (And How To Avoid Them) 32/568 - 03 Nov 2023
 Why Is Billable Viable Product An Alternative To Minimum Viable Product? 31/200
Why Is Billable Viable Product An Alternative To Minimum Viable Product? 31/200 - 16 Oct 2025
 AI Inference Explained Simply: What Developers Really Need to Know 30/58
AI Inference Explained Simply: What Developers Really Need to Know 30/58 - 28 Nov 2025
 How AI Will Transform Vendor Onboarding and Seller Management in 2026 30/82
How AI Will Transform Vendor Onboarding and Seller Management in 2026 30/82 - 15 Aug 2024
 Digital Governance vs IT Governance: What’s the Difference and Why It Matters 29/81
Digital Governance vs IT Governance: What’s the Difference and Why It Matters 29/81 - 01 Sep 2022
 Facts Chart: Why Do Software Projects Fail? 29/596
Facts Chart: Why Do Software Projects Fail? 29/596 - 01 Mar 2023
 What is Unit Testing? Pros and cons of Unit Testing? 29/439
What is Unit Testing? Pros and cons of Unit Testing? 29/439 - 19 Oct 2021
 Software development life cycles 29/701
Software development life cycles 29/701 - 16 Dec 2025
 Reducing Cognitive Friction in Software Development: A Guide to Faster, Happier Teams 28/77
Reducing Cognitive Friction in Software Development: A Guide to Faster, Happier Teams 28/77 - 10 Sep 2024
 Leading Remote Teams in Hybrid Work Environments 27/160
Leading Remote Teams in Hybrid Work Environments 27/160 - 05 Jun 2025
 How AI-Driven Computer Vision Is Changing the Face of Retail Analytics 26/135
How AI-Driven Computer Vision Is Changing the Face of Retail Analytics 26/135 - 07 Nov 2025
 Online vs. Offline Machine Learning Courses in South Africa: Which One Should You Pick? 25/70
Online vs. Offline Machine Learning Courses in South Africa: Which One Should You Pick? 25/70 - 16 Oct 2024
 7 Game-Changing Features of InstaDoodle: The Ultimate AI Doodle Video Maker 25/63
7 Game-Changing Features of InstaDoodle: The Ultimate AI Doodle Video Maker 25/63 - 10 Apr 2022
 Difference Between Forward and Backward Reasoning in AI 25/1683
Difference Between Forward and Backward Reasoning in AI 25/1683 - 18 Oct 2024
 IT Governance, IT Management and IT Outsourcing: What’s the Difference? 24/71
IT Governance, IT Management and IT Outsourcing: What’s the Difference? 24/71 - 14 Aug 2024
 From Steel to Software: The Reluctant Evolution of Japan's Tech Corporates 24/545
From Steel to Software: The Reluctant Evolution of Japan's Tech Corporates 24/545 - 25 Dec 2025
 What Is Algorithmic Fairness? Who Determines the Value of Content: Humans or Algorithms? 23/47
What Is Algorithmic Fairness? Who Determines the Value of Content: Humans or Algorithms? 23/47 - 23 Dec 2024
 Garbage In, Megabytes Out (GIMO): How to Rise Above AI Slop and Create Real Signal 23/60
Garbage In, Megabytes Out (GIMO): How to Rise Above AI Slop and Create Real Signal 23/60 - 31 Dec 2025
 10 Skills to Make You "Irreplaceable" in the Next 3 Years (even if AI changes everything) 22/34
10 Skills to Make You "Irreplaceable" in the Next 3 Years (even if AI changes everything) 22/34 - 21 Nov 2025
 The Rise of AgentOps: How Enterprises Are Managing and Scaling AI Agents 22/69
The Rise of AgentOps: How Enterprises Are Managing and Scaling AI Agents 22/69 - 11 Oct 2022
 Why choose Billable Viable Product (BVP) over Minimum Viable Product (MVP) 22/361
Why choose Billable Viable Product (BVP) over Minimum Viable Product (MVP) 22/361 - 20 Mar 2022
 What is a Multi-Model Database? Pros and Cons? 21/1164
What is a Multi-Model Database? Pros and Cons? 21/1164 - 24 Dec 2024
 Artificial Intelligence and Cybersecurity: Building Trust in EFL Tutoring 20/180
Artificial Intelligence and Cybersecurity: Building Trust in EFL Tutoring 20/180 - 17 Mar 2025
 Integrating Salesforce with Yardi: A Guide to Achieving Success in Real Estate Business 19/202
Integrating Salesforce with Yardi: A Guide to Achieving Success in Real Estate Business 19/202 - 02 May 2022
 Difference between CapEx vs. OpEx: Two Ways to Finance Your Software Project 19/1524
Difference between CapEx vs. OpEx: Two Ways to Finance Your Software Project 19/1524 - 16 Apr 2021
 Insightful Business Technology Consulting at TIGO 18/412
Insightful Business Technology Consulting at TIGO 18/412 - 21 Dec 2023
 Top 12 Low-Code Platforms To Use in 2024 18/1248
Top 12 Low-Code Platforms To Use in 2024 18/1248 - 23 Jun 2025
 AI Avatars in the Metaverse: How Digital Beings Are Redefining Identity and Social Interaction 18/125
AI Avatars in the Metaverse: How Digital Beings Are Redefining Identity and Social Interaction 18/125 - 09 Jul 2024
 What Is Artificial Intelligence and How Is It Used Today? 18/243
What Is Artificial Intelligence and How Is It Used Today? 18/243 - 03 Dec 2025
 IT Outsourcing Solutions Explained: What, How, Why, When 18/40
IT Outsourcing Solutions Explained: What, How, Why, When 18/40 - 13 Oct 2025
 Dora AI: Turn Prompts Into Pixel-Perfect Websites-No Code, No Limits 18/63
Dora AI: Turn Prompts Into Pixel-Perfect Websites-No Code, No Limits 18/63 - 12 Jan 2026
 Companies Developing Custom AI Models for Brand Creative: Market Landscape and Use Cases 18/29
Companies Developing Custom AI Models for Brand Creative: Market Landscape and Use Cases 18/29 - 07 Oct 2025
 Case Study: Using the “Messaging House” Framework to Build a Digital Transformation Roadmap 17/86
Case Study: Using the “Messaging House” Framework to Build a Digital Transformation Roadmap 17/86 - 18 Aug 2024
 The Future of Web Development: Emerging Trends and Technologies Every Developer Should Know 17/201
The Future of Web Development: Emerging Trends and Technologies Every Developer Should Know 17/201 - 05 Sep 2023
 The Cold Start Problem: How to Start and Scale Network Effects 17/203
The Cold Start Problem: How to Start and Scale Network Effects 17/203 - 29 Oct 2024
 Top AI Tools and Frameworks You’ll Master in an Artificial Intelligence Course 17/385
Top AI Tools and Frameworks You’ll Master in an Artificial Intelligence Course 17/385 - 22 Nov 2024
 The Role of AI in Enhancing Business Efficiency and Decision-Making 17/196
The Role of AI in Enhancing Business Efficiency and Decision-Making 17/196 - 04 Oct 2021
 Product Validation: The Key to Developing the Best Product Possible 17/320
Product Validation: The Key to Developing the Best Product Possible 17/320 - 03 Jul 2022
 What is the difference between Project Proposal and Software Requirements Specification (SRS) in software engineering? 17/1025
What is the difference between Project Proposal and Software Requirements Specification (SRS) in software engineering? 17/1025 - 05 Mar 2021
 How do you minimize risks when you outsource software development? 16/336
How do you minimize risks when you outsource software development? 16/336 - 31 Dec 2021
 What is a Data Pipeline? 16/215
What is a Data Pipeline? 16/215 - 31 Aug 2022
 What are the best practices for software contract negotiations? 16/260
What are the best practices for software contract negotiations? 16/260 - 20 Feb 2025
 How Machine Learning is Shaping the Future of Digital Advertising 16/123
How Machine Learning is Shaping the Future of Digital Advertising 16/123 - 02 Dec 2024
 The Intersection of AI and Business Analytics: Key Concepts to Master in Your Business Analytics Course 15/295
The Intersection of AI and Business Analytics: Key Concepts to Master in Your Business Analytics Course 15/295 - 18 Jul 2024
 The 8 Best ways to Innovate your SAAS Business Model in 2024 15/257
The 8 Best ways to Innovate your SAAS Business Model in 2024 15/257 - 27 Jul 2024
 Positive Psychology in the Digital Age: Future Directions and Technologies 15/408
Positive Psychology in the Digital Age: Future Directions and Technologies 15/408 - 17 Oct 2025
 MLOps vs AIOps: What’s the Difference and Why It Matters 15/100
MLOps vs AIOps: What’s the Difference and Why It Matters 15/100 - 10 Apr 2022
 What is predictive analytics? Why it matters? 15/192
What is predictive analytics? Why it matters? 15/192 - 31 Dec 2022
 The New Normal for Software Development 15/364
The New Normal for Software Development 15/364 - 21 Jun 2022
 Difference between Quality and Grade 15/801
Difference between Quality and Grade 15/801 - 22 Sep 2022
 Why is it important to have a “single point of contact (SPoC)” on an IT project? 14/939
Why is it important to have a “single point of contact (SPoC)” on an IT project? 14/939 - 30 Jan 2022
 What Does a Sustaining Engineer Do? 14/617
What Does a Sustaining Engineer Do? 14/617 - 07 Aug 2022
 Things to Consider When Choosing a Technology Partner 14/283
Things to Consider When Choosing a Technology Partner 14/283 - 08 Nov 2022
 4 tips for meeting tough deadlines when outsourcing projects to software vendor 14/291
4 tips for meeting tough deadlines when outsourcing projects to software vendor 14/291 - 25 Apr 2021
 What is outstaffing? 14/270
What is outstaffing? 14/270 - 10 Nov 2025
 Multi-Modal AI Agents: Merging Voice, Text, and Vision for Better CX 14/97
Multi-Modal AI Agents: Merging Voice, Text, and Vision for Better CX 14/97 - 10 Jul 2025
 Building AI-Driven Knowledge Graphs from Unstructured Data 14/163
Building AI-Driven Knowledge Graphs from Unstructured Data 14/163 - 07 Jul 2021
 The 5 Levels of IT Help Desk Support 13/448
The 5 Levels of IT Help Desk Support 13/448 - 13 Nov 2021
 What Is Bleeding Edge Technology? Are bleeding edge technologies cheaper? 13/539
What Is Bleeding Edge Technology? Are bleeding edge technologies cheaper? 13/539 - 28 Jul 2022
 POC, Prototypes, Pilots and MVP: What Are the Differences? 13/697
POC, Prototypes, Pilots and MVP: What Are the Differences? 13/697 - 31 Dec 2023
 Software Development Outsourcing Trends to Watch Out for in 2024 13/233
Software Development Outsourcing Trends to Watch Out for in 2024 13/233 - 15 Aug 2023
 Production-Ready vs Feature-Complete: What’s the Difference? 12/227
Production-Ready vs Feature-Complete: What’s the Difference? 12/227 - 02 Jan 2024
 What is User Provisioning & Deprovisioning? 12/554
What is User Provisioning & Deprovisioning? 12/554 - 28 Oct 2022
 Build Operate Transfer (B.O.T) Model in Software Outsourcing 12/405
Build Operate Transfer (B.O.T) Model in Software Outsourcing 12/405 - 17 Jun 2021
 What is IT-business alignment? 12/374
What is IT-business alignment? 12/374 - 10 Apr 2021
 RFP vs POC: Why the proof of concept is replacing the request for proposal 12/322
RFP vs POC: Why the proof of concept is replacing the request for proposal 12/322 - 01 Feb 2022
 Outstaffing Vs. Outsourcing: What’s The Difference? 12/595
Outstaffing Vs. Outsourcing: What’s The Difference? 12/595 - 20 Aug 2025
 What Is Agentic AI? The Next Phase of Artificial Intelligence 12/149
What Is Agentic AI? The Next Phase of Artificial Intelligence 12/149 - 25 Jan 2025
 The Decline of Traditional SaaS and the Rise of AI-first Applications 12/109
The Decline of Traditional SaaS and the Rise of AI-first Applications 12/109 - 09 Oct 2024
 Short-Form Video Advertising: The Secret to Captivating Your Audience 12/134
Short-Form Video Advertising: The Secret to Captivating Your Audience 12/134 - 24 Oct 2025
 AI Agents in SaaS Platforms: Automating User Support and Onboarding 12/77
AI Agents in SaaS Platforms: Automating User Support and Onboarding 12/77 - 10 Sep 2024
 AI in Email Marketing: Personalization and Automation 11/183
AI in Email Marketing: Personalization and Automation 11/183 - 05 May 2022
 DAM vs. CMS: What's the difference? 11/489
DAM vs. CMS: What's the difference? 11/489 - 06 Mar 2021
 4 things you need to do before getting an accurate quote for your software development 11/679
4 things you need to do before getting an accurate quote for your software development 11/679 - 03 Nov 2022
 Top questions and answers you must know before ask for software outsourcing 11/292
Top questions and answers you must know before ask for software outsourcing 11/292 - 04 Oct 2022
 Which ERP implementation strategy is right for your business? 11/313
Which ERP implementation strategy is right for your business? 11/313 - 25 Jan 2022
 What is the difference between Outsourcing and Outstaffing? 11/334
What is the difference between Outsourcing and Outstaffing? 11/334 - 16 Feb 2021
 Choose Outsourcing for Your Non Disclosure Agreement (NDA) 11/173
Choose Outsourcing for Your Non Disclosure Agreement (NDA) 11/173 - 02 Nov 2021
 Difference between an ESTIMATE and a QUOTE 11/362
Difference between an ESTIMATE and a QUOTE 11/362 - 16 Sep 2022
 Examples Of Augmented Intelligence In Today’s Workplaces Shaping the Business as Usual 10/436
Examples Of Augmented Intelligence In Today’s Workplaces Shaping the Business as Usual 10/436 - 06 Jun 2024
 Software Upgrade vs Software Update: What is the difference? 10/250
Software Upgrade vs Software Update: What is the difference? 10/250 - 03 Jan 2024
 Why Partnership is important for Growth? 10/159
Why Partnership is important for Growth? 10/159 - 12 Dec 2021
 Zero Sum Games Agile vs. Waterfall Project Management Methods 10/409
Zero Sum Games Agile vs. Waterfall Project Management Methods 10/409 - 05 Aug 2024
 Revisiting the Mistake That Halted Japan's Software Surge 10/342
Revisiting the Mistake That Halted Japan's Software Surge 10/342 - 31 Jul 2025
 Top WooCommerce Pre-Order Plugins with Countdown & Discounts 10/93
Top WooCommerce Pre-Order Plugins with Countdown & Discounts 10/93 - 06 May 2025
 How Machine Learning Is Transforming Data Analytics Workflows 10/187
How Machine Learning Is Transforming Data Analytics Workflows 10/187 - 18 Jul 2021
 How To Ramp Up An Offshore Software Development Team Quickly 9/593
How To Ramp Up An Offshore Software Development Team Quickly 9/593 - 19 Dec 2023
 How AI is Transforming Software Development? 9/294
How AI is Transforming Software Development? 9/294 - 18 Mar 2022
 Difference between Project Management and Management Consulting 9/356
Difference between Project Management and Management Consulting 9/356 - 16 Aug 2022
 What is a Headless CMS? 8/272
What is a Headless CMS? 8/272 - 24 Nov 2021
 What is the difference between off-the-shelf software and customized software? 8/443
What is the difference between off-the-shelf software and customized software? 8/443 - 09 Mar 2022
 Consultant Implementation Pricing 8/213
Consultant Implementation Pricing 8/213 - 09 Jan 2022
 How to Bridge the Gap Between Business and IT? 8/178
How to Bridge the Gap Between Business and IT? 8/178 - 21 Aug 2024
 What is Singularity and Its Impact on Businesses? 8/403
What is Singularity and Its Impact on Businesses? 8/403 - 22 Sep 2025
 Why AI Is Critical for Accelerating Drug Discovery in Pharma 8/83
Why AI Is Critical for Accelerating Drug Discovery in Pharma 8/83 - 04 Oct 2023
 The Future of Work: Harnessing AI Solutions for Business Growth 7/275
The Future of Work: Harnessing AI Solutions for Business Growth 7/275 - 06 Mar 2024
 [SemRush] What Are LSI Keywords & Why They Don‘t Matter 7/176
[SemRush] What Are LSI Keywords & Why They Don‘t Matter 7/176 - 21 Apr 2025
 Agent AI in Multimodal Interaction: Transforming Human-Computer Engagement 7/188
Agent AI in Multimodal Interaction: Transforming Human-Computer Engagement 7/188 - 01 Apr 2022
 Dedicated Team vs. Extended Team: What’s the difference? 7/328
Dedicated Team vs. Extended Team: What’s the difference? 7/328 - 15 Sep 2022
 CRM vs CDP: What's the difference? 7/268
CRM vs CDP: What's the difference? 7/268 - 09 Dec 2021
 Customer Service vs Technical Support: What’s The Difference? 7/302
Customer Service vs Technical Support: What’s The Difference? 7/302 - 01 Mar 2023
 How do you deal with disputes and conflicts that may arise during a software consulting project? 7/165
How do you deal with disputes and conflicts that may arise during a software consulting project? 7/165 - 15 Apr 2024
 Weights & Biases: The AI Developer Platform 7/189
Weights & Biases: The AI Developer Platform 7/189 - 07 Oct 2022
 Digital Transformation: Become a Technology Powerhouse 6/244
Digital Transformation: Become a Technology Powerhouse 6/244 - 27 Aug 2025
 How AI Consulting Is Driving Smarter Diagnostics and Hospital Operations 6/100
How AI Consulting Is Driving Smarter Diagnostics and Hospital Operations 6/100 - 30 Jul 2024
 The Future of IT Consulting: Trends and Opportunities 6/190
The Future of IT Consulting: Trends and Opportunities 6/190 - 12 Aug 2024
 Understanding Google Analytics in Mumbai: A Beginner's Guide 6/99
Understanding Google Analytics in Mumbai: A Beginner's Guide 6/99 - 25 Sep 2024
 Enhancing Decision-Making Skills with an MBA: Data-Driven Approaches for Business Growth 6/201
Enhancing Decision-Making Skills with an MBA: Data-Driven Approaches for Business Growth 6/201 - 29 Aug 2025
 How AI Is Transforming Modern Management Science 5/46
How AI Is Transforming Modern Management Science 5/46 - 30 Oct 2022
 How Much Does MVP Development Cost in 2023? 5/240
How Much Does MVP Development Cost in 2023? 5/240 - 01 May 2023
 CTO Interview Questions 5/329
CTO Interview Questions 5/329 - 18 Jan 2024
 Self-healing code is the future of software development 5/213
Self-healing code is the future of software development 5/213 - 09 Feb 2023
 The Challenge of Fixed-Bid Software Projects 5/213
The Challenge of Fixed-Bid Software Projects 5/213 - 20 Nov 2022
 Software Requirements Are A Communication Problem 5/244
Software Requirements Are A Communication Problem 5/244 - 01 Dec 2023
 Laws of Project Management 5/302
Laws of Project Management 5/302 - 31 Dec 2022
 Future of Software Development Trends and Predictions 5/143
Future of Software Development Trends and Predictions 5/143 - 15 Aug 2025
 Quantum Technology: Global Challenges and Opportunities for Innovators 4/100
Quantum Technology: Global Challenges and Opportunities for Innovators 4/100 - 27 Feb 2025
 How AI Agents are Changing Software Development? 4/186
How AI Agents are Changing Software Development? 4/186 - 17 Mar 2025
 IT Consultants in Digital Transformation 3/84
IT Consultants in Digital Transformation 3/84 - 01 May 2024
 Warren Buffett’s Golden Rule for Digital Transformation: Avoiding Tech Overload 3/205
Warren Buffett’s Golden Rule for Digital Transformation: Avoiding Tech Overload 3/205 - 10 Nov 2021
 PoC vs. Prototype vs. MVP: What’s the difference? 3/807
PoC vs. Prototype vs. MVP: What’s the difference? 3/807 - 05 Aug 2024
 Affordable Tech: How Chatbots Enhance Value in Healthcare Software 2/169
Affordable Tech: How Chatbots Enhance Value in Healthcare Software 2/169
Artificial Intelligence vs. Machine Learning: A Deep Dive into Their Applications and Use Cases
With the rapid developments in AI and ML today, the danger of conflating these two is at an all-time high. They are the cornerstone of the innovations of our time, from the simpler implementations like the virtual assistants on our smartphones to the more complex self-driving vehicle algorithms. As much as they are related, the difference is there. Grasping their differences is important for a technology expert, a company executive and even a person who is thinking of taking up a specialized Artificial Intelligence Course or a Machine Learning Course.
In this article, I will explain the fundamental differences between AI and ML and outline their distinctive applications along with related use cases, so that the impact they have to us in our life can be truly appreciated.
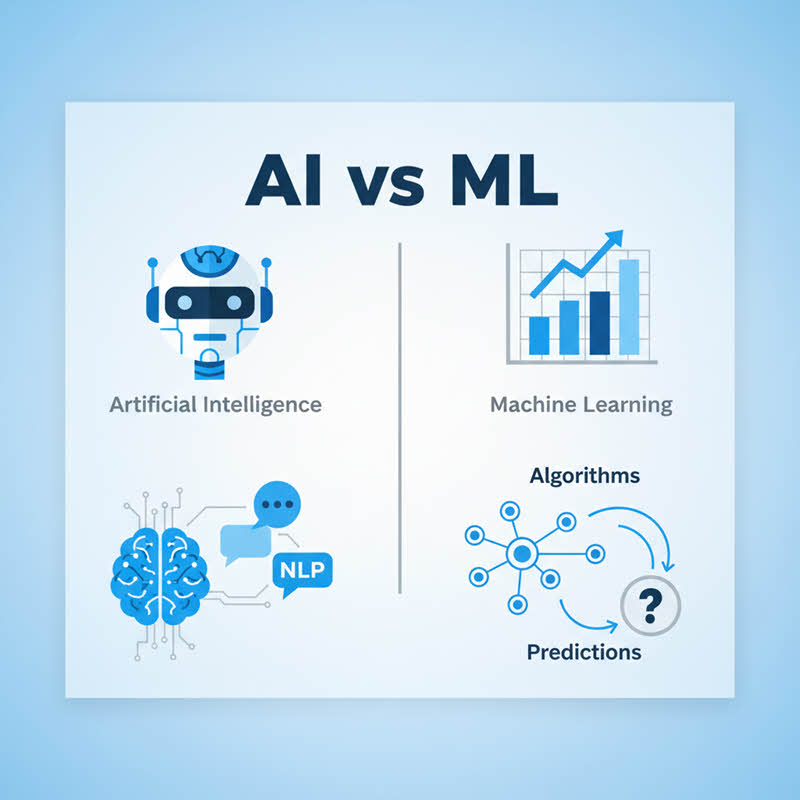
Unpacking the Concepts: AI vs. ML
Artificial Intelligence is the more general, overarching field. It is the science of making machines or systems that perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and even language understanding. Consider AI the end-goal—building intelligent agents that operate independently and make decisions.
Machine Learning is a specific and very useful subset of AI. It is a means of creating artificial intelligence. Instead of being programmed a certain way with certain rules for every situation, ML systems are built to learn from data. The more data, the more they improve, over time. This learning capacity is the game changer. It enables machines to determine patterns, predictions, and learn from new data without continually having to be told what to do by humans.
The analogy that can help clarify what we mean by AI/ML is simply this: AI is the umbrella, and ML is a very substantial, high tech tool under the umbrella. You can have AI, and not be able to do ML (e.g. rule-based expert systems), but you can't have ML without it being an offshoot of AI. For anyone entering a career in this area, understanding this relationship is your first, best step. It is a foundational point made in any respectable artificial intelligence course.
Applications and Use Cases of Artificial Intelligence
There is a wide variety of AI use cases and capabilities that are not limited to predictive modeling. Ultimately, it is about creating a smart solution to help address some of the biggest challenges across the globe. Below we highlight some of the most frequently noted use cases and those being used in real life now.
1. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP is the branch of AI that enables computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language.
- Use Case: Virtual Assistants and Chatbots. Virtual assistants like Siri, Google Assistant, and Amazon Alexa use natural language processing (NLP) to "hear" our command, understand the intent of the user and respond with the appropriate response. Similarly, chatbots on websites utilize NLP to answer customer support cases, process orders, and provide information in spoken form.
- Use Case: Machine Translation. Programs like Google Translate use AI to process the inputs of one language to interpret the syntax and context translating this into an accurate target language.
2. Computer Vision
This area of AI demonstrates the ability for machines to "see" and understand visual inputs from images or video. It is an essential part of a large variety of technologies in use today.
- Use Case: Autonomous vehicles. Self-driving cars or trucks are heavily dependent on computer vision. The system is using real-time video data from cameras to understand the "world" around it; for example, identifying pedestrians, traffic signs, other cars, lane markings all in order to make driving decisions.
- Use Case: Medical imaging analysis. AI systems are learning to analyze medical images like x-rays, MRIs, and CT scans and find subtle patterns that likely indicate something such as cancer, often faster, and better, than a human radiologist.
3. Robotics
AI in robotics is about fashioning robots that can remark their atmosphere, learn from it, and make verdicts to perform tasks.
- Use Case: Manufacturing and Logistics. Occasionally, robots powered by artificial intelligence will do repetitive and precise tasks in factories with tasks such as welding and assembly and even quality control. In logistics, robots operate autonomously in warehouses to refine and transport packages, improving efficiency.
- Use Case: Surgical Robots. In health care, robotic systems relying on AI can help surgeons by offering a steady hand, increased precision, and perform minimally invasive procedures.
Applications and Use Cases of Machine Learning
While AI is the brain, Machine Learning is the learning engine. Machine Learning applications focus on analyzing data, recognizing patterns and making predictions. This is where a good Machine Learning Course is worth its weight in gold, because it's all about building and training models.
1. Predictive Analytics
This is one of the most mutual and powerful submissions of ML. It involves using numerical algorithms to analyze historical data and forecast future outcomes.
- Use Case: Fraud Detection. Financial entities utilize ML to monitor every transaction in real-time. The models use large data sets from the past when fraudulent activity occurred to find unusual patterns such as a purchase that was unusually large for one individual purchasing or a transaction that occurred in a new area, and flagged as suspected fraud.
- Use Case: Credit Risk Assessment. Banks and lending companies use ML to check the creditworthiness of an applicant for a loan. The algorithm takes into account a person's financial history of payment and request for loans which were used to ascertain and determine the likelihood of default which aids in deciding the extent to which they play an influential role in a lending decision that is fair lending decisions.
2. Recommendation Engines
These organizations use ML to analyze user behaviour and predilections to suggest products, contented, or services they might like.
- Use Case: E-commerce. When you shop on Amazon and see "Customers who bought this item also bought..." information it is an output of a ML recommendation engine. The recommendation engine looks at all the items you have purchased in the past and what you browsed when you shopped and provides recommendations on related or relevant items, which increases their sales tremendously.
- Use Case: Entertainment. Similarly, streaming sites like Netflix and Spotify utilize complex ML algorithms to suggest movies or shows or music that are based on everything you have viewed or listened to, in addition to similar viewer’s preferences. The recommendations make your experience more personalized and are critical to the user's ability to stay engaged and return to the site.
3. Spam Filters and Cybersecurity
ML algorithms are repetitively at work in arrears the scenes to protect us from uninvited content and malicious attacks.
- Use Case: Email Spam Filtering. An excellent example of a supervised ML model is your email service's spam filter. It is trained, using labelled emails indicating spam or not spam (as millions of spam emails are) to learn how to discern junk mail. It is trained to automatically recognize the qualities of spam, such as specific keywords, sender domain(s), and types of attachments to recognize junk mail, and it moves them to a junk mail folder.
- Use Case: Network Security. ML models are also being used to identify anomalies in network traffic for the possibility of a cyber-attack. They learn "normal" behaviour of the network and become aware and can identify relatively quickly, when something abnormal is occurring simply when a large number of login attempts are not normal, or data access is not normal.
The Symbiosis: When AI and ML Work Together
It is important to understand that, in many cases, AI and ML do not exist in privacy; they work collaboratively. A smart home assistant is an excellent example. It has one general goal an intelligent assistant that will respond to your questions, control devices, and manage your schedule which is a defined Artificial Intelligence task. The underlying engine that allows it to recognize your voice and learn your likes/dislikes is Machine Learning.
Similarly, a self-driving car is an artificial intelligence system. The system relies on multiple ML models to accomplish its various tasks, using a computer vision model to recognize objects that are present, a predictive model that forecasts other driver's actions, and a reinforcement learning model to train itself to be a better driver. The Artificial Intelligence Course that you may take will look at the broad strokes of the overall system, and a Machine Learning Course will teach you how to build and tune the individual components.
Final Thoughts: Choosing Your Path
The difference between AI and ML is more than just a difference in terminology; it represents a distinction in the different levels of complexity in the technology and degree of specialization in terms of careers. Having taken an Artificial Intelligence Course will give you a broad overview of the principles of intelligent systems, while training in a Machine Learning Course will gain you the practical ability, technical skill, and hands-on experience required to build the data-driven models for many of today’s most innovative applications.
There is an increasing demand and need for workers, candidates, professionals, etc., to find and develop talented individuals for roles where both AI and ML are required. Whether intentional or not, fittingly the push towards developing capabilities related to Artificial intelligence and Machine Learning (ML) is turning into an equivalent cultural and technological challenge. You may want to design true human-like intelligent autonomous machines and systems, or simply build a better spam filter. But it all starts with a solid education. The future is built on these systems and technologies. The first step towards participation, acceptance, and engagement is understanding the constructive qualities distinctive to Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML).



























 Link copied!
Link copied!
 Recently Updated News
Recently Updated News