Kaizen and DMAIC: What's the differences?
Published on: August 20, 2022
Last updated: January 06, 2023 Read in fullscreen view
Last updated: January 06, 2023 Read in fullscreen view
- 10 Apr 2022
 Agile self-organizing teams: What are they? How do they work? 51/535
Agile self-organizing teams: What are they? How do they work? 51/535 - 21 May 2022
 "Fail Fast, Fail Often, Fail Forward" is the answer to Agile practices of software success 34/1027
"Fail Fast, Fail Often, Fail Forward" is the answer to Agile practices of software success 34/1027 - 27 Oct 2020
 8 principles of Agile Testing 31/1309
8 principles of Agile Testing 31/1309 - 17 Dec 2025
 Unaligned Escalation Logic: A Silent Risk in Complex Organizations 22/39
Unaligned Escalation Logic: A Silent Risk in Complex Organizations 22/39 - 12 Oct 2020
 The Agile Manifesto - Principle #8 20/496
The Agile Manifesto - Principle #8 20/496 - 20 Jan 2021
 Fail early, fail often, fail cheap, fail safe but always fail forward 20/750
Fail early, fail often, fail cheap, fail safe but always fail forward 20/750 - 02 Nov 2021
 [Case Study] Streamlined Data Reporting using Tableau 20/309
[Case Study] Streamlined Data Reporting using Tableau 20/309 - 03 Jul 2022
 Manifesto for Agile Software Development 18/276
Manifesto for Agile Software Development 18/276 - 20 Jan 2022
 TIGO Self-Organization Practice: Change Management Workflow 18/471
TIGO Self-Organization Practice: Change Management Workflow 18/471 - 02 Dec 2022
 Success Story: Satsuki - Sales Management Software, back office app for School Subscription Management 17/248
Success Story: Satsuki - Sales Management Software, back office app for School Subscription Management 17/248 - 11 Nov 2021
 What is an IT Self-service Portal? Why is it Important to Your Business? 16/427
What is an IT Self-service Portal? Why is it Important to Your Business? 16/427 - 13 Feb 2021
 Why is TIGOSOFT a software house for Enterprise Application Development? 15/362
Why is TIGOSOFT a software house for Enterprise Application Development? 15/362 - 01 Jan 2024
 The pros and cons of the Centralized Enterprise Automation Operating model 14/224
The pros and cons of the Centralized Enterprise Automation Operating model 14/224 - 03 Sep 2022
 The secret of software success: Simplicity is the ultimate sophistication 14/214
The secret of software success: Simplicity is the ultimate sophistication 14/214 - 06 Nov 2023
 How do you streamline requirement analysis and modeling? 12/223
How do you streamline requirement analysis and modeling? 12/223 - 01 Mar 2022
 Why Does Scrum Fail in Large Companies? 11/265
Why Does Scrum Fail in Large Companies? 11/265 - 07 Oct 2020
 How To Manage Expectations at Work (and Why It's Important) 11/306
How To Manage Expectations at Work (and Why It's Important) 11/306 - 09 Oct 2022
 Key Advantages and Disadvantages of Agile Methodology 11/697
Key Advantages and Disadvantages of Agile Methodology 11/697 - 16 Jun 2022
 Rapid Application Development (RAD): Pros and Cons 9/866
Rapid Application Development (RAD): Pros and Cons 9/866 - 03 Apr 2021
 How digital asset management streamlines your content workflow? 9/333
How digital asset management streamlines your content workflow? 9/333 - 20 Nov 2022
 Agile working method in software and football 9/344
Agile working method in software and football 9/344 - 02 Nov 2022
 Frequently Asked Questions about Agile and Scrum 8/399
Frequently Asked Questions about Agile and Scrum 8/399 - 21 Oct 2022
 Virtual meeting - How does TIGO save cost, reduce complexity and improve quality by remote communication? 8/191
Virtual meeting - How does TIGO save cost, reduce complexity and improve quality by remote communication? 8/191 - 16 Jul 2022
 What are disadvantages of Agile Methodology? How to mitigate the disadvantages ? 8/377
What are disadvantages of Agile Methodology? How to mitigate the disadvantages ? 8/377 - 01 Dec 2022
 Difference between Set-based development and Point-based development 8/346
Difference between Set-based development and Point-based development 8/346 - 01 Jun 2022
 How Your Agile Development Team is Just Like a Football Team? 7/224
How Your Agile Development Team is Just Like a Football Team? 7/224 - 10 Oct 2022
 Should Your Business Go Agile? (Infographic) 6/128
Should Your Business Go Agile? (Infographic) 6/128 - 21 Jun 2021
 6 Useful Tips To Streamline Business Processes and Workflows 6/528
6 Useful Tips To Streamline Business Processes and Workflows 6/528 - 04 Mar 2023
 [Medium] Box-Ticking: The Management Strategy That’s Killing your Productivity 6/600
[Medium] Box-Ticking: The Management Strategy That’s Killing your Productivity 6/600 - 28 Nov 2023
 Scrum Team Failure — Scrum Anti-Patterns Taxonomy 5/253
Scrum Team Failure — Scrum Anti-Patterns Taxonomy 5/253
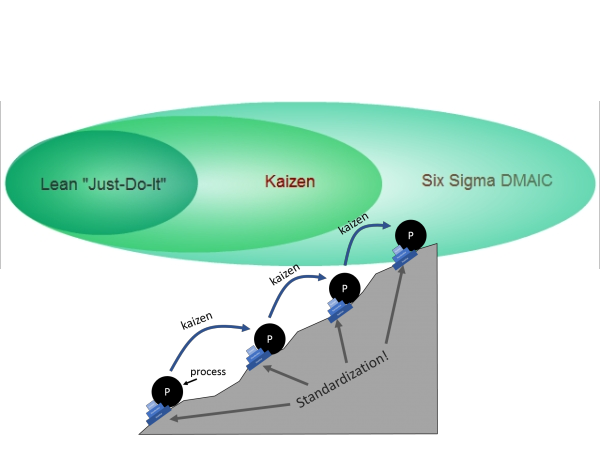
Let’s look at the main characteristics of each approach:
Kaizen™ – a Japanese word that simply means ‘Change for the better’. The main characteristics are:
- Projects are well defined and baseline stats are collected before starting
- Dedicated resources are subject matter experts (SMEs) and focus on only the project
- The solutions should come from the SMEs as they will need to act as champions for the change
- Often follows the Demming/Shewhart cycle of Plan-Do-Check-Act
- Kaizen™ projects typically last 3 – 5 days
- Management MUST make resources available from support functions during the project. i.e., HR, Finance, Warehouse, Sales, Marketing
- Solutions are implemented based on 80% confidence instead of 95%
- Implementation is completed within the project timeline but if items fall outside, they are generally completed within 20 days
- Basic analysis is acceptable with indicative results enough to make decisions.
After the Kaizen event the following activities are recommended:
- Walkthroughs are conducted with the process area team
- Follow up with Future State process owner
- Updated Process Metrics, measure, and data
- To-Do list follow up
- The final measure of controlled metrics evaluated
- Training and SOP verification
DMAIC – a 5-step process where the 1st letter of each stage spells out DMAIC: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control. The main characteristics are:
- The existing process is not meeting customer requirements, but the reason why is not obvious
- Time is spent on analyzing the baseline data to understand current performance
- Baseline data is used to prove/validate the benefits once re-measured
- Solutions can come from anywhere and may not be popular with employees as they may mean significant changes
- Solutions require 95% confidence in being correct before implementation
- There can be a level of risk associated with the solution that will need to be accepted by the business before implementation
- Change is led by a Six Sigma Blackbelt or Greenbelt due to the nature of the data analysis.
[{"displaySettingInfo":"[{\"isFullLayout\":false,\"layoutWidthRatio\":\"\",\"isFaqLayout\":false,\"isIncludedCaption\":false,\"faqLayoutTheme\":\"1\",\"isSliderLayout\":false}]"},{"articleSourceInfo":"[{\"sourceName\":\"\",\"sourceValue\":\"\"}]"},{"privacyInfo":"[{\"isOutsideVietnam\":false}]"},{"tocInfo":"[{\"isEnabledTOC\":true,\"isAutoNumbering\":false,\"isShowKeyHeadingWithIcon\":false}]"}]
Via
{content}




























 Link copied!
Link copied!
 Recently Updated News
Recently Updated News