Why Does Scrum Fail in Large Companies?
Last updated: November 05, 2023 Read in fullscreen view
- 10 Apr 2022
 Agile self-organizing teams: What are they? How do they work? 51/535
Agile self-organizing teams: What are they? How do they work? 51/535 - 18 Oct 2020
 How to use the "Knowns" and "Unknowns" technique to manage assumptions 38/1089
How to use the "Knowns" and "Unknowns" technique to manage assumptions 38/1089 - 21 May 2022
 "Fail Fast, Fail Often, Fail Forward" is the answer to Agile practices of software success 34/1027
"Fail Fast, Fail Often, Fail Forward" is the answer to Agile practices of software success 34/1027 - 27 Oct 2020
 8 principles of Agile Testing 31/1309
8 principles of Agile Testing 31/1309 - 01 Oct 2020
 Fail fast, learn faster with Agile methodology 24/1047
Fail fast, learn faster with Agile methodology 24/1047 - 14 Oct 2021
 Advantages and Disadvantages of Time and Material Contract (T&M) 22/864
Advantages and Disadvantages of Time and Material Contract (T&M) 22/864 - 12 Oct 2020
 The Agile Manifesto - Principle #8 20/496
The Agile Manifesto - Principle #8 20/496 - 13 Dec 2020
 Move fast, fail fast, fail-safe 20/323
Move fast, fail fast, fail-safe 20/323 - 18 Aug 2022
 What are the consequences of poor requirements with software development projects? 20/274
What are the consequences of poor requirements with software development projects? 20/274 - 06 Feb 2021
 Why fail fast and learn fast? 19/450
Why fail fast and learn fast? 19/450 - 03 Jul 2022
 Manifesto for Agile Software Development 18/276
Manifesto for Agile Software Development 18/276 - 23 Sep 2021
 INFOGRAPHIC: Top 9 Software Outsourcing Mistakes 17/439
INFOGRAPHIC: Top 9 Software Outsourcing Mistakes 17/439 - 01 Mar 2023
 Bug Prioritization - What are the 5 levels of priority? 16/234
Bug Prioritization - What are the 5 levels of priority? 16/234 - 10 Nov 2022
 Poor Code Indicators and How to Improve Your Code? 16/231
Poor Code Indicators and How to Improve Your Code? 16/231 - 19 Oct 2021
 Is gold plating good or bad in project management? 15/816
Is gold plating good or bad in project management? 15/816 - 19 Apr 2021
 7 Most Common Time-Wasters For Software Development 14/556
7 Most Common Time-Wasters For Software Development 14/556 - 31 Oct 2021
 Tips to Fail Fast With Outsourcing 12/392
Tips to Fail Fast With Outsourcing 12/392 - 08 Oct 2022
 KPI - The New Leadership 12/602
KPI - The New Leadership 12/602 - 07 Oct 2020
 How To Manage Expectations at Work (and Why It's Important) 11/306
How To Manage Expectations at Work (and Why It's Important) 11/306 - 09 Oct 2022
 Key Advantages and Disadvantages of Agile Methodology 11/697
Key Advantages and Disadvantages of Agile Methodology 11/697 - 10 Dec 2023
 Pain points of User Acceptance Testing (UAT) 11/452
Pain points of User Acceptance Testing (UAT) 11/452 - 17 Feb 2022
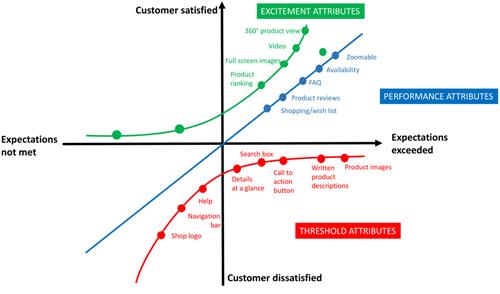
 Prioritizing Software Requirements with Kano Analysis 10/304
Prioritizing Software Requirements with Kano Analysis 10/304 - 28 Dec 2021
 8 types of pricing models in software development outsourcing 10/437
8 types of pricing models in software development outsourcing 10/437 - 05 Jan 2024
 Easy ASANA tips & tricks for you and your team 9/200
Easy ASANA tips & tricks for you and your team 9/200 - 11 Jan 2024
 What are the Benefits and Limitations of Augmented Intelligence? 9/477
What are the Benefits and Limitations of Augmented Intelligence? 9/477 - 20 Nov 2022
 Agile working method in software and football 9/344
Agile working method in software and football 9/344 - 12 Mar 2024
 How do you create FOMO in software prospects? 9/167
How do you create FOMO in software prospects? 9/167 - 01 Dec 2022
 Difference between Set-based development and Point-based development 8/346
Difference between Set-based development and Point-based development 8/346 - 02 Nov 2022
 Frequently Asked Questions about Agile and Scrum 8/399
Frequently Asked Questions about Agile and Scrum 8/399 - 21 Oct 2022
 Virtual meeting - How does TIGO save cost, reduce complexity and improve quality by remote communication? 8/191
Virtual meeting - How does TIGO save cost, reduce complexity and improve quality by remote communication? 8/191 - 16 Jul 2022
 What are disadvantages of Agile Methodology? How to mitigate the disadvantages ? 7/376
What are disadvantages of Agile Methodology? How to mitigate the disadvantages ? 7/376 - 01 Jun 2022
 How Your Agile Development Team is Just Like a Football Team? 7/224
How Your Agile Development Team is Just Like a Football Team? 7/224 - 10 Oct 2022
 Should Your Business Go Agile? (Infographic) 6/128
Should Your Business Go Agile? (Infographic) 6/128 - 14 Mar 2024
 Why should you opt for software localization from a professional agency? 6/140
Why should you opt for software localization from a professional agency? 6/140 - 06 Nov 2019
 How to Access Software Project Size? 6/249
How to Access Software Project Size? 6/249 - 26 Dec 2023
 Improving Meeting Effectiveness Through the Six Thinking Hats 5/253
Improving Meeting Effectiveness Through the Six Thinking Hats 5/253 - 28 Nov 2023
 Scrum Team Failure — Scrum Anti-Patterns Taxonomy 5/253
Scrum Team Failure — Scrum Anti-Patterns Taxonomy 5/253
-
Lack of executive support
One of the primary reasons for Scrum's failure in large organizations is the lack of support from the executive leadership team. Scrum requires a significant culture change and requires the leadership team to be fully committed to its principles and practices. When this support is not present, the implementation of Scrum can quickly become disjointed and ineffective.
-
Silos and hierarchical structures
Large organizations often have complex hierarchical structures and silos that can make it difficult for Scrum teams to work effectively. Scrum relies on cross-functional teams and continuous collaboration, but when teams are separated by departmental boundaries, this can lead to misunderstandings, miscommunications, and ultimately, project failures.
-
Resistance to change
Change is hard, and introducing a new way of working can be met with resistance, particularly in large organizations where processes and policies have been in place for a long time. This resistance can come from both team members and management, and can make it difficult to fully embrace and implement Scrum practices.
-
Inflexibility
Scrum is an Agile methodology, which means that it requires a high degree of flexibility and adaptability. However, in large organizations, processes and procedures can become rigid, and it can be difficult to change course when necessary. This inflexibility can lead to a lack of agility and make it difficult to implement Scrum effectively.
-
Complexity of projects
Scrum is designed to manage smaller, less complex projects, and its practices may not scale well to larger, more complex projects. In these cases, teams may struggle to manage the work, and it can be difficult to maintain a high level of transparency and collaboration.
-
Lack of proper training
To implement Scrum effectively, teams need to have a thorough understanding of its principles and practices. In large organizations, it can be challenging to provide the necessary training to all team members, which can result in a lack of understanding and ineffective implementation of the methodology.
-
Inadequate resources
Scrum requires a significant investment in terms of time and resources to implement effectively. In large organizations, it can be difficult to allocate the necessary resources to support Scrum practices, particularly in a culture that prioritizes efficiency and cost-saving.































 Link copied!
Link copied!
 Recently Updated News
Recently Updated News