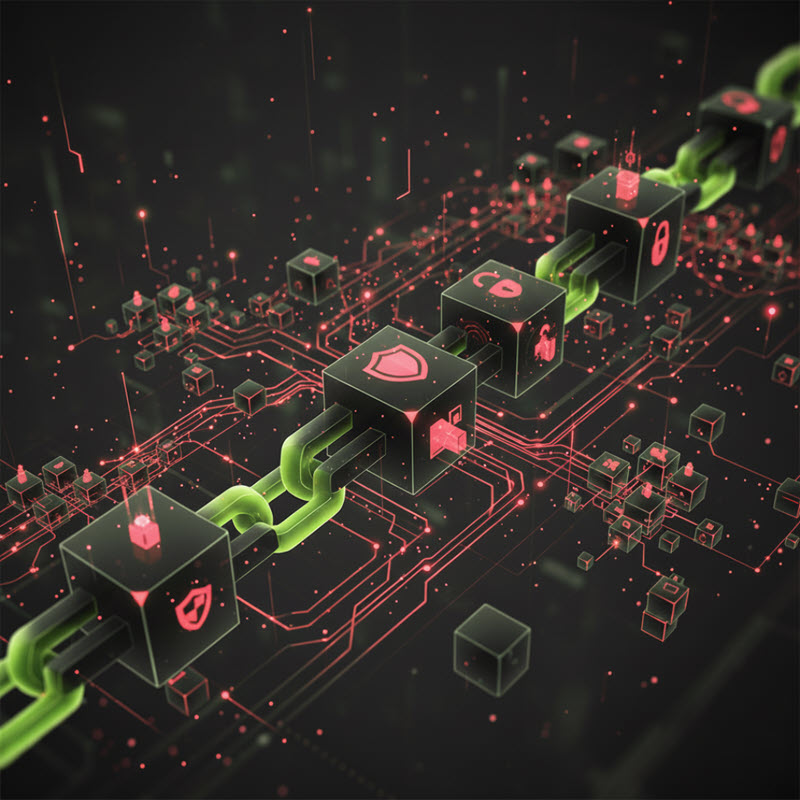

Blockchain Explained: Key Advantages and Limitations You Should Know
Last updated: November 25, 2025 Read in fullscreen view
- 05 Oct 2025
 The New Facebook Algorithm: A Paradigm Shift in Content Discovery 66/109
The New Facebook Algorithm: A Paradigm Shift in Content Discovery 66/109 - 17 Jul 2023
 What Is SSL? A Simple Explanation Even a 10-Year-Old Can Understand 41/119
What Is SSL? A Simple Explanation Even a 10-Year-Old Can Understand 41/119 - 01 Dec 2025
 Manufacturing 4.0: AI Agents Enabling Self-Optimizing Production Systems 39/76
Manufacturing 4.0: AI Agents Enabling Self-Optimizing Production Systems 39/76 - 05 Jul 2020
 What is Sustaining Software Engineering? 38/1301
What is Sustaining Software Engineering? 38/1301 - 03 Oct 2025
 Top CMS Trends 2026: The Future of Digital Content Management 37/55
Top CMS Trends 2026: The Future of Digital Content Management 37/55 - 20 Dec 2025
 The Future of IT Consulting: Key Trends for 2026–2030 35/67
The Future of IT Consulting: Key Trends for 2026–2030 35/67 - 03 Nov 2023
 Why Is Billable Viable Product An Alternative To Minimum Viable Product? 31/200
Why Is Billable Viable Product An Alternative To Minimum Viable Product? 31/200 - 01 Mar 2023
 What is Unit Testing? Pros and cons of Unit Testing? 29/439
What is Unit Testing? Pros and cons of Unit Testing? 29/439 - 10 Sep 2024
 Leading Remote Teams in Hybrid Work Environments 27/160
Leading Remote Teams in Hybrid Work Environments 27/160 - 11 Oct 2022
 Why choose Billable Viable Product (BVP) over Minimum Viable Product (MVP) 22/361
Why choose Billable Viable Product (BVP) over Minimum Viable Product (MVP) 22/361 - 31 Dec 2025
 10 Skills to Make You "Irreplaceable" in the Next 3 Years (even if AI changes everything) 22/34
10 Skills to Make You "Irreplaceable" in the Next 3 Years (even if AI changes everything) 22/34 - 20 Mar 2022
 What is a Multi-Model Database? Pros and Cons? 21/1164
What is a Multi-Model Database? Pros and Cons? 21/1164 - 17 Mar 2025
 Integrating Salesforce with Yardi: A Guide to Achieving Success in Real Estate Business 19/202
Integrating Salesforce with Yardi: A Guide to Achieving Success in Real Estate Business 19/202 - 23 Jun 2025
 AI Avatars in the Metaverse: How Digital Beings Are Redefining Identity and Social Interaction 18/125
AI Avatars in the Metaverse: How Digital Beings Are Redefining Identity and Social Interaction 18/125 - 21 Dec 2023
 Top 12 Low-Code Platforms To Use in 2024 18/1248
Top 12 Low-Code Platforms To Use in 2024 18/1248 - 03 Jul 2022
 What is the difference between Project Proposal and Software Requirements Specification (SRS) in software engineering? 17/1025
What is the difference between Project Proposal and Software Requirements Specification (SRS) in software engineering? 17/1025 - 22 Nov 2024
 The Role of AI in Enhancing Business Efficiency and Decision-Making 17/196
The Role of AI in Enhancing Business Efficiency and Decision-Making 17/196 - 18 Aug 2024
 The Future of Web Development: Emerging Trends and Technologies Every Developer Should Know 17/201
The Future of Web Development: Emerging Trends and Technologies Every Developer Should Know 17/201 - 20 Feb 2025
 How Machine Learning is Shaping the Future of Digital Advertising 16/123
How Machine Learning is Shaping the Future of Digital Advertising 16/123 - 03 Jan 2026
 The Hidden Rules of IT Project Tendering: Laws, Principles, and Caveats You Must Know 15/28
The Hidden Rules of IT Project Tendering: Laws, Principles, and Caveats You Must Know 15/28 - 06 Nov 2025
 DataOps: The Next Frontier in Agile Data Management 15/64
DataOps: The Next Frontier in Agile Data Management 15/64 - 02 Dec 2024
 The Intersection of AI and Business Analytics: Key Concepts to Master in Your Business Analytics Course 15/295
The Intersection of AI and Business Analytics: Key Concepts to Master in Your Business Analytics Course 15/295 - 31 Dec 2021
 What is a Data Pipeline? 15/214
What is a Data Pipeline? 15/214 - 10 Apr 2022
 What is predictive analytics? Why it matters? 15/192
What is predictive analytics? Why it matters? 15/192 - 31 Dec 2022
 The New Normal for Software Development 15/364
The New Normal for Software Development 15/364 - 25 Apr 2021
 What is outstaffing? 14/270
What is outstaffing? 14/270 - 22 Sep 2022
 Why is it important to have a “single point of contact (SPoC)” on an IT project? 14/939
Why is it important to have a “single point of contact (SPoC)” on an IT project? 14/939 - 30 Jan 2022
 What Does a Sustaining Engineer Do? 14/617
What Does a Sustaining Engineer Do? 14/617 - 18 Jul 2024
 The 8 Best ways to Innovate your SAAS Business Model in 2024 14/256
The 8 Best ways to Innovate your SAAS Business Model in 2024 14/256 - 27 Jul 2024
 Positive Psychology in the Digital Age: Future Directions and Technologies 14/407
Positive Psychology in the Digital Age: Future Directions and Technologies 14/407 - 13 Nov 2021
 What Is Bleeding Edge Technology? Are bleeding edge technologies cheaper? 13/539
What Is Bleeding Edge Technology? Are bleeding edge technologies cheaper? 13/539 - 31 Dec 2023
 Software Development Outsourcing Trends to Watch Out for in 2024 13/233
Software Development Outsourcing Trends to Watch Out for in 2024 13/233 - 25 Jan 2025
 The Decline of Traditional SaaS and the Rise of AI-first Applications 12/109
The Decline of Traditional SaaS and the Rise of AI-first Applications 12/109 - 09 Oct 2024
 Short-Form Video Advertising: The Secret to Captivating Your Audience 12/134
Short-Form Video Advertising: The Secret to Captivating Your Audience 12/134 - 20 Aug 2025
 What Is Agentic AI? The Next Phase of Artificial Intelligence 12/149
What Is Agentic AI? The Next Phase of Artificial Intelligence 12/149 - 10 Sep 2024
 AI in Email Marketing: Personalization and Automation 10/182
AI in Email Marketing: Personalization and Automation 10/182 - 03 Jan 2024
 Why Partnership is important for Growth? 10/159
Why Partnership is important for Growth? 10/159 - 16 Sep 2022
 Examples Of Augmented Intelligence In Today’s Workplaces Shaping the Business as Usual 10/436
Examples Of Augmented Intelligence In Today’s Workplaces Shaping the Business as Usual 10/436 - 16 Sep 2022
 Examples Of Augmented Intelligence In Today’s Workplaces Shaping the Business as Usual 10/436
Examples Of Augmented Intelligence In Today’s Workplaces Shaping the Business as Usual 10/436 - 19 Dec 2023
 How AI is Transforming Software Development? 9/294
How AI is Transforming Software Development? 9/294 - 09 Sep 2025
 Aligning BI Dashboards with KPIs: A Business + Data Collaboration Guide 8/79
Aligning BI Dashboards with KPIs: A Business + Data Collaboration Guide 8/79 - 16 Aug 2022
 What is a Headless CMS? 8/272
What is a Headless CMS? 8/272 - 13 Jan 2024
 The “Rule of Law” in Software Projects: Engineering Principles That Govern Successful Development 8/21
The “Rule of Law” in Software Projects: Engineering Principles That Govern Successful Development 8/21 - 16 Aug 2022
 What is a Headless CMS? 8/272
What is a Headless CMS? 8/272 - 25 Sep 2024
 Enhancing Decision-Making Skills with an MBA: Data-Driven Approaches for Business Growth 6/201
Enhancing Decision-Making Skills with an MBA: Data-Driven Approaches for Business Growth 6/201 - 30 Jul 2024
 The Future of IT Consulting: Trends and Opportunities 6/190
The Future of IT Consulting: Trends and Opportunities 6/190 - 31 Dec 2022
 Future of Software Development Trends and Predictions 5/143
Future of Software Development Trends and Predictions 5/143 - 18 Jan 2024
 Self-healing code is the future of software development 5/213
Self-healing code is the future of software development 5/213 - 27 Feb 2025
 How AI Agents are Changing Software Development? 4/186
How AI Agents are Changing Software Development? 4/186
Exploring the Pros and Cons of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain has become one of the most talked-about technologies in the digital world. Although it has existed for decades, it continues to draw attention because of its potential to transform how we store data, manage transactions, and build trust across the internet. To understand blockchain better, let’s explore its key strengths and weaknesses in a simple and practical way.
What Is Blockchain?
Blockchain first appeared in 1991, but it truly rose to global recognition in 2009 thanks to Bitcoin—the first cryptocurrency built using blockchain. At its core, blockchain is a system that stores information in “blocks,” which are linked together in a secure and chronological chain. Every block is connected tightly to the next, making the entire system resistant to tampering or unauthorized changes.
What makes blockchain different from traditional systems is its decentralized structure. Instead of storing data on a single server, blockchain distributes it across many computers (nodes) around the world. This design improves security, protects privacy, and eliminates the need for third-party verification in many applications.
The Pros and Cons of Blockchain Technology
Advantages of Blockchain
1. Decentralized and Secure Data
Blockchain stores data across multiple nodes. If one node fails or is attacked, the information remains safe in other nodes. This decentralization helps prevent hacking, data loss, and single points of failure—issues that often occur in centralized databases.
2. High Stability and Tamper Resistance
All nodes constantly update their copies of the blockchain, ensuring that the data is accurate and almost impossible to manipulate. Once information is added, it becomes a permanent record.
3. Reduced Operational Costs
Because blockchain removes the need for intermediaries, businesses can significantly lower costs. Transactions are verified by the network, eliminating fees paid to third-party service providers.
4. Transparency and Trust
Blockchain networks operate under strict participation rules. Every authorized user can track and verify transactions, making the system transparent, auditable, and trustworthy.
Limitations of Blockchain
1. Data Is Hard to Modify
The same immutability that makes blockchain secure also makes it inflexible. Updating past data requires complex procedures such as hard forks, which can be costly and disruptive.
2. Risk of 51% Attacks
If someone gains control of more than 50% of a blockchain network’s computing power, they can manipulate transactions. While uncommon, this risk remains one of blockchain’s major security concerns.
3. High Setup and Maintenance Costs
Building and operating a blockchain system—especially a private or enterprise-grade chain—requires strong infrastructure, specialized skills, and ongoing maintenance, which can be expensive.
4. Asset Loss Due to Private Key Exposure
Blockchain relies on cryptographic private keys. If a user loses their private key or it becomes exposed, they could lose access to their digital assets permanently.
5. Growing Storage Requirements
Blockchains increase in size over time. For example, the Bitcoin blockchain already requires hundreds of gigabytes to store. This growth can discourage individuals from running nodes, reducing decentralization.
Conclusion
Blockchain is not perfect, but its potential is undeniable. From finance and banking to supply chain management, logistics, and retail, blockchain offers new ways to build secure, transparent, and efficient systems. Understanding both sides of blockchain technology helps businesses and users make smarter decisions about how to apply it in the future.













26072024043639_thumb.jpg)















 Link copied!
Link copied!
 Recently Updated News
Recently Updated News