Manufacturing 4.0: AI Agents Enabling Self-Optimizing Production Systems
Last updated: December 08, 2025 Read in fullscreen view
- 14 Jan 2026
 How to Evaluate the Business and Productivity Software Company Seismic on RFP AI Agent Use Cases 84/97
How to Evaluate the Business and Productivity Software Company Seismic on RFP AI Agent Use Cases 84/97 - 05 Oct 2025
 The New Facebook Algorithm: A Paradigm Shift in Content Discovery 66/109
The New Facebook Algorithm: A Paradigm Shift in Content Discovery 66/109 - 06 Dec 2025
 Enterprise Operations 2.0: Why AI Agents Are Replacing Traditional Automation 48/83
Enterprise Operations 2.0: Why AI Agents Are Replacing Traditional Automation 48/83 - 23 Dec 2025
 Microsoft Power Automate vs. n8n: What’s the Real Difference? 47/77
Microsoft Power Automate vs. n8n: What’s the Real Difference? 47/77 - 25 Nov 2025
 How AI Agents Are Redefining Enterprise Automation and Decision-Making 46/96
How AI Agents Are Redefining Enterprise Automation and Decision-Making 46/96 - 06 Nov 2025
 Top 10 AI Development Companies in the USA to Watch in 2026 41/90
Top 10 AI Development Companies in the USA to Watch in 2026 41/90 - 01 Jul 2025
 The Hidden Costs of Not Adopting AI Agents: Risk of Falling Behind 37/163
The Hidden Costs of Not Adopting AI Agents: Risk of Falling Behind 37/163 - 02 Dec 2025
 The Question That Shook Asia: What Happens When We Ask AI to Choose Between a Mother and a Wife? 37/63
The Question That Shook Asia: What Happens When We Ask AI to Choose Between a Mother and a Wife? 37/63 - 03 Oct 2025
 Top CMS Trends 2026: The Future of Digital Content Management 37/55
Top CMS Trends 2026: The Future of Digital Content Management 37/55 - 20 Dec 2025
 The Future of IT Consulting: Key Trends for 2026–2030 35/67
The Future of IT Consulting: Key Trends for 2026–2030 35/67 - 22 Dec 2025
 The Role of Automotive Software in Building Smarter Vehicles 35/59
The Role of Automotive Software in Building Smarter Vehicles 35/59 - 03 Nov 2023
 Why Is Billable Viable Product An Alternative To Minimum Viable Product? 31/200
Why Is Billable Viable Product An Alternative To Minimum Viable Product? 31/200 - 16 Oct 2025
 AI Inference Explained Simply: What Developers Really Need to Know 30/58
AI Inference Explained Simply: What Developers Really Need to Know 30/58 - 28 Nov 2025
 How AI Will Transform Vendor Onboarding and Seller Management in 2026 30/82
How AI Will Transform Vendor Onboarding and Seller Management in 2026 30/82 - 16 Dec 2025
 Reducing Cognitive Friction in Software Development: A Guide to Faster, Happier Teams 28/77
Reducing Cognitive Friction in Software Development: A Guide to Faster, Happier Teams 28/77 - 02 Oct 2022
 The Real Factors Behind Bill Gates’ Success: Luck, Skills, or Connections? 28/361
The Real Factors Behind Bill Gates’ Success: Luck, Skills, or Connections? 28/361 - 10 Sep 2024
 Leading Remote Teams in Hybrid Work Environments 27/160
Leading Remote Teams in Hybrid Work Environments 27/160 - 29 Jan 2026
 Why Headless Commerce Is Shaping the Future of the Online Store 27/35
Why Headless Commerce Is Shaping the Future of the Online Store 27/35 - 05 Jun 2025
 How AI-Driven Computer Vision Is Changing the Face of Retail Analytics 26/135
How AI-Driven Computer Vision Is Changing the Face of Retail Analytics 26/135 - 07 Nov 2025
 Online vs. Offline Machine Learning Courses in South Africa: Which One Should You Pick? 25/70
Online vs. Offline Machine Learning Courses in South Africa: Which One Should You Pick? 25/70 - 23 Dec 2024
 Garbage In, Megabytes Out (GIMO): How to Rise Above AI Slop and Create Real Signal 23/60
Garbage In, Megabytes Out (GIMO): How to Rise Above AI Slop and Create Real Signal 23/60 - 25 Dec 2025
 What Is Algorithmic Fairness? Who Determines the Value of Content: Humans or Algorithms? 23/47
What Is Algorithmic Fairness? Who Determines the Value of Content: Humans or Algorithms? 23/47 - 31 Dec 2025
 10 Skills to Make You "Irreplaceable" in the Next 3 Years (even if AI changes everything) 22/34
10 Skills to Make You "Irreplaceable" in the Next 3 Years (even if AI changes everything) 22/34 - 21 Nov 2025
 The Rise of AgentOps: How Enterprises Are Managing and Scaling AI Agents 22/69
The Rise of AgentOps: How Enterprises Are Managing and Scaling AI Agents 22/69 - 11 Oct 2022
 Why choose Billable Viable Product (BVP) over Minimum Viable Product (MVP) 22/361
Why choose Billable Viable Product (BVP) over Minimum Viable Product (MVP) 22/361 - 24 Dec 2024
 Artificial Intelligence and Cybersecurity: Building Trust in EFL Tutoring 20/180
Artificial Intelligence and Cybersecurity: Building Trust in EFL Tutoring 20/180 - 23 Jun 2025
 AI Avatars in the Metaverse: How Digital Beings Are Redefining Identity and Social Interaction 18/125
AI Avatars in the Metaverse: How Digital Beings Are Redefining Identity and Social Interaction 18/125 - 21 Dec 2023
 Top 12 Low-Code Platforms To Use in 2024 18/1248
Top 12 Low-Code Platforms To Use in 2024 18/1248 - 09 Jul 2024
 What Is Artificial Intelligence and How Is It Used Today? 18/243
What Is Artificial Intelligence and How Is It Used Today? 18/243 - 12 Jan 2026
 Companies Developing Custom AI Models for Brand Creative: Market Landscape and Use Cases 18/29
Companies Developing Custom AI Models for Brand Creative: Market Landscape and Use Cases 18/29 - 18 Aug 2024
 The Future of Web Development: Emerging Trends and Technologies Every Developer Should Know 17/201
The Future of Web Development: Emerging Trends and Technologies Every Developer Should Know 17/201 - 29 Oct 2024
 Top AI Tools and Frameworks You’ll Master in an Artificial Intelligence Course 17/385
Top AI Tools and Frameworks You’ll Master in an Artificial Intelligence Course 17/385 - 22 Nov 2024
 The Role of AI in Enhancing Business Efficiency and Decision-Making 17/196
The Role of AI in Enhancing Business Efficiency and Decision-Making 17/196 - 20 Feb 2025
 How Machine Learning is Shaping the Future of Digital Advertising 16/123
How Machine Learning is Shaping the Future of Digital Advertising 16/123 - 02 Dec 2024
 The Intersection of AI and Business Analytics: Key Concepts to Master in Your Business Analytics Course 15/295
The Intersection of AI and Business Analytics: Key Concepts to Master in Your Business Analytics Course 15/295 - 27 Jul 2024
 Positive Psychology in the Digital Age: Future Directions and Technologies 15/408
Positive Psychology in the Digital Age: Future Directions and Technologies 15/408 - 31 Dec 2022
 The New Normal for Software Development 15/364
The New Normal for Software Development 15/364 - 06 Nov 2025
 DataOps: The Next Frontier in Agile Data Management 15/64
DataOps: The Next Frontier in Agile Data Management 15/64 - 17 Oct 2025
 MLOps vs AIOps: What’s the Difference and Why It Matters 15/100
MLOps vs AIOps: What’s the Difference and Why It Matters 15/100 - 10 Nov 2025
 Multi-Modal AI Agents: Merging Voice, Text, and Vision for Better CX 14/97
Multi-Modal AI Agents: Merging Voice, Text, and Vision for Better CX 14/97 - 18 Jul 2024
 The 8 Best ways to Innovate your SAAS Business Model in 2024 14/256
The 8 Best ways to Innovate your SAAS Business Model in 2024 14/256 - 31 Dec 2023
 Software Development Outsourcing Trends to Watch Out for in 2024 13/233
Software Development Outsourcing Trends to Watch Out for in 2024 13/233 - 09 Oct 2024
 Short-Form Video Advertising: The Secret to Captivating Your Audience 12/134
Short-Form Video Advertising: The Secret to Captivating Your Audience 12/134 - 25 Jan 2025
 The Decline of Traditional SaaS and the Rise of AI-first Applications 12/109
The Decline of Traditional SaaS and the Rise of AI-first Applications 12/109 - 24 Oct 2025
 AI Agents in SaaS Platforms: Automating User Support and Onboarding 12/77
AI Agents in SaaS Platforms: Automating User Support and Onboarding 12/77 - 20 Aug 2025
 What Is Agentic AI? The Next Phase of Artificial Intelligence 12/149
What Is Agentic AI? The Next Phase of Artificial Intelligence 12/149 - 10 Sep 2024
 AI in Email Marketing: Personalization and Automation 11/183
AI in Email Marketing: Personalization and Automation 11/183 - 03 Jan 2024
 Why Partnership is important for Growth? 10/159
Why Partnership is important for Growth? 10/159 - 16 Sep 2022
 Examples Of Augmented Intelligence In Today’s Workplaces Shaping the Business as Usual 10/436
Examples Of Augmented Intelligence In Today’s Workplaces Shaping the Business as Usual 10/436 - 06 May 2025
 How Machine Learning Is Transforming Data Analytics Workflows 10/187
How Machine Learning Is Transforming Data Analytics Workflows 10/187 - 31 Jul 2025
 Top WooCommerce Pre-Order Plugins with Countdown & Discounts 10/93
Top WooCommerce Pre-Order Plugins with Countdown & Discounts 10/93 - 16 Sep 2022
 Examples Of Augmented Intelligence In Today’s Workplaces Shaping the Business as Usual 10/436
Examples Of Augmented Intelligence In Today’s Workplaces Shaping the Business as Usual 10/436 - 19 Dec 2023
 How AI is Transforming Software Development? 9/294
How AI is Transforming Software Development? 9/294 - 16 Aug 2022
 What is a Headless CMS? 8/272
What is a Headless CMS? 8/272 - 21 Aug 2024
 What is Singularity and Its Impact on Businesses? 8/403
What is Singularity and Its Impact on Businesses? 8/403 - 09 Sep 2025
 Aligning BI Dashboards with KPIs: A Business + Data Collaboration Guide 8/79
Aligning BI Dashboards with KPIs: A Business + Data Collaboration Guide 8/79 - 22 Sep 2025
 Why AI Is Critical for Accelerating Drug Discovery in Pharma 8/83
Why AI Is Critical for Accelerating Drug Discovery in Pharma 8/83 - 16 Aug 2022
 What is a Headless CMS? 8/272
What is a Headless CMS? 8/272 - 04 Oct 2023
 The Future of Work: Harnessing AI Solutions for Business Growth 7/275
The Future of Work: Harnessing AI Solutions for Business Growth 7/275 - 21 Apr 2025
 Agent AI in Multimodal Interaction: Transforming Human-Computer Engagement 7/188
Agent AI in Multimodal Interaction: Transforming Human-Computer Engagement 7/188 - 15 Apr 2024
 Weights & Biases: The AI Developer Platform 7/189
Weights & Biases: The AI Developer Platform 7/189 - 30 Jul 2024
 The Future of IT Consulting: Trends and Opportunities 6/190
The Future of IT Consulting: Trends and Opportunities 6/190 - 25 Sep 2024
 Enhancing Decision-Making Skills with an MBA: Data-Driven Approaches for Business Growth 6/201
Enhancing Decision-Making Skills with an MBA: Data-Driven Approaches for Business Growth 6/201 - 27 Aug 2025
 How AI Consulting Is Driving Smarter Diagnostics and Hospital Operations 6/100
How AI Consulting Is Driving Smarter Diagnostics and Hospital Operations 6/100 - 29 Aug 2025
 How AI Is Transforming Modern Management Science 5/46
How AI Is Transforming Modern Management Science 5/46 - 31 Dec 2022
 Future of Software Development Trends and Predictions 5/143
Future of Software Development Trends and Predictions 5/143 - 18 Jan 2024
 Self-healing code is the future of software development 5/213
Self-healing code is the future of software development 5/213 - 27 Feb 2025
 How AI Agents are Changing Software Development? 4/186
How AI Agents are Changing Software Development? 4/186 - 15 Aug 2025
 Quantum Technology: Global Challenges and Opportunities for Innovators 4/100
Quantum Technology: Global Challenges and Opportunities for Innovators 4/100 - 05 Aug 2024
 Affordable Tech: How Chatbots Enhance Value in Healthcare Software 2/169
Affordable Tech: How Chatbots Enhance Value in Healthcare Software 2/169
| About the Author | Anand Subramanian | Technology expert and AI enthusiast |
Anand Subramanian is a technology expert and AI enthusiast currently leading the marketing function at Intellectyx, a Data, Digital, and AI solutions provider with over a decade of experience working with enterprises and government departments. |
Manufacturing is entering a pivotal era. Global supply chains are unstable, demand fluctuations are unpredictable, labor availability is shrinking, and compliance mandates are tightening. Traditional automation PLC-driven workflows, predefined machine rules, SCADA operations, and robotics have carried the industry forward for decades. But today, leaders face a sobering reality:
Factories are more automated than ever, yet operational inefficiencies remain stubbornly high.
According to McKinsey:
- 65% of manufacturers still experience unplanned downtime every month
- Over 40% of production decisions are made using incomplete data
- Manufacturers lose $3M per hour on average due to downtime (IDC)
The root cause? Traditional automation was built for fixed processes, not the dynamic, multi-variable, unpredictable environments that define modern manufacturing.
As plants become more digital, interconnected, and complex, the limitations of deterministic systems are becoming impossible to ignore. Manufacturers no longer need more automation; they need intelligent autonomy. They need AI Agents.
This is the foundation of Manufacturing 4.0, where factories become self-optimizing, self-correcting, and increasingly self-sufficient.
Why Traditional Automation Can No Longer Carry the Weight
Before we explore the rise of AI Agents, it’s important to understand why the old model is breaking down.
1. Static Rules in a Dynamic Environment
Automation systems depend on fixed logic and parameters. But manufacturing conditions, machine wear, temperature fluctuations, input variability are rarely static.
When a sensor drifts or an input material changes quality, systems fail, production slows, or operators must manually intervene.
2. Siloed Data Sources
Production data lives in:
- MES
- SCADA
- PLC logs
- Quality systems
- ERP
- Maintenance systems
None of these ecosystem components speak to each other in real-time.
AI Agents unify and interpret all of these data streams to operate holistically.
3. Rising Maintenance and Integration Costs
Adding more automation does not simplify operations, it complicates them.
Manufacturers are spending:
- 30 50% of automation budgets on maintenance and patching
- Millions per year on integration contracts
AI Agents reduce maintenance drastically by adapting autonomously.
4. Human Expertise Bottleneck
Skilled technicians and operators are becoming harder to find and retain.
AI Agents preserve operational knowledge and independently execute tasks previously requiring expert judgment.
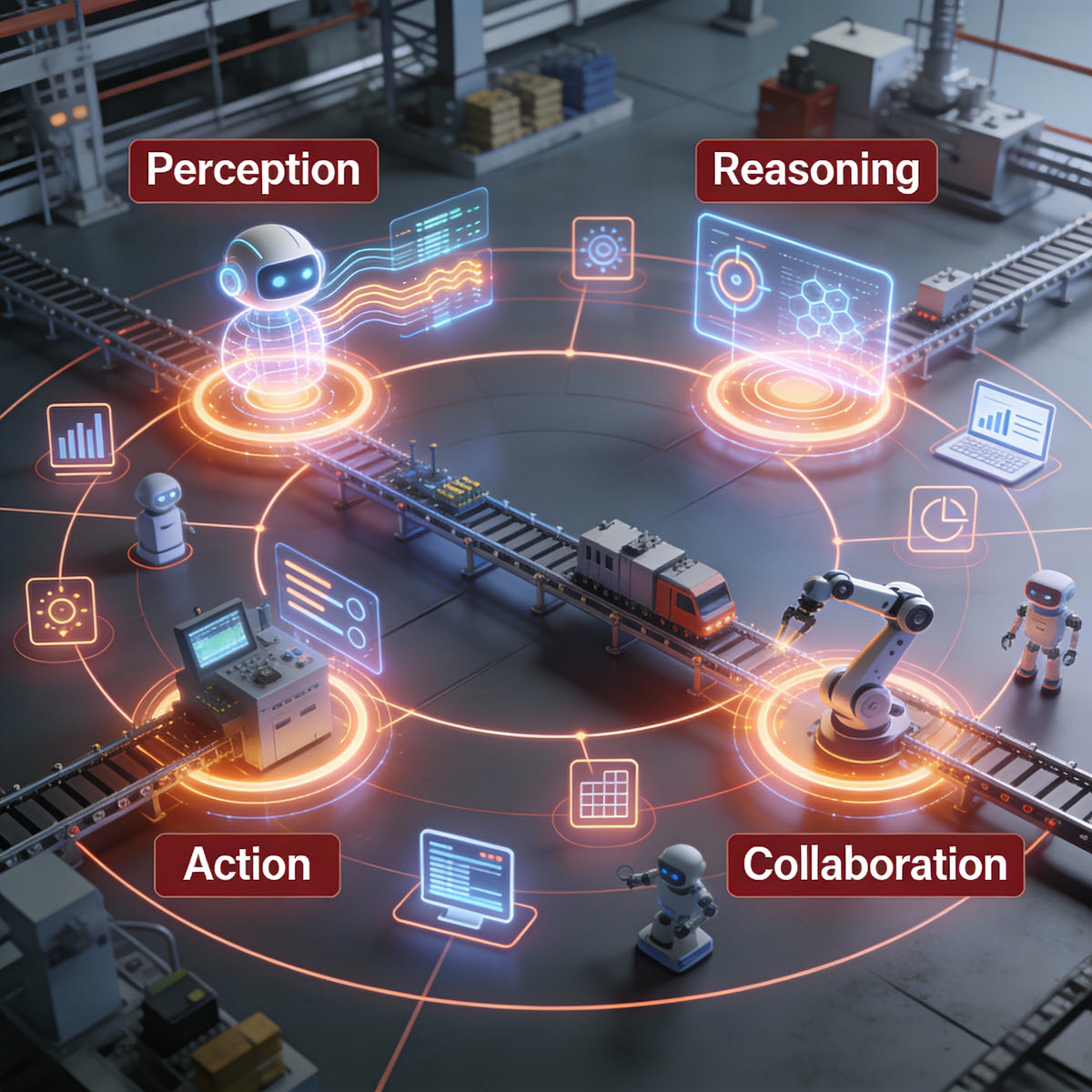
AI Agents: The Engine Behind Self-Optimizing Production Systems
Unlike traditional automation, AI Agents are dynamic, autonomous decision-making entities that can perceive, reason, and act across production environments.
They operate with four foundational capabilities:
1. Perception
Understand structured and unstructured data from sensors, logs, documents, and machine interfaces.
2. Reasoning
Interpret conditions, identify patterns, diagnose root causes, and plan actions.
3. Action
Execute tasks autonomously adjust machine parameters, modify schedules, trigger maintenance workflows, instruct robots, update MES.
4. Collaboration
Coordinate with other AI agents to optimize production holistically.
This is the backbone of self-optimizing systems factories that continuously monitor, learn, predict, and adjust without human intervention.
The Manufacturing 4.0 AI Agent Stack
Imagine this as a vertical stack (textual form):
Layer 1: Multimodal AI Perception
AI agents read and interpret:
- Sensor streams
- SCADA/PLC data
- Vision data
- Maintenance logs
- Quality inspection images
- Supply chain feeds
- Operator notes
Layer 2: Cognitive Manufacturing Intelligence
Agents use:
- LLM reasoning
- Predictive models
- Digital twins
- Anomaly detection
- Root-cause algorithms
- Domain-specific rule engines
Layer 3: Autonomous Execution
Agents autonomously control:
- Machine parameters
- Work order sequencing
- Energy consumption
- Predictive maintenance actions
- Quality adjustments
- Production rescheduling
Layer 4: Governance & Human-in-the-Loop
Ensures:
- Safety compliance
- Supervisory control
- Escalation workflows
- Audit logs
- Policy adherence
This stack forms the architecture of intelligent, resilient Manufacturing 4.0 operations.
Where AI Agents Outperform Traditional Automation (Table)
| Attribute | Traditional Automation | AI Agents |
|---|---|---|
| Logic | Rule-based | Adaptive, context-aware |
| Reaction to Variability | Low | High |
| Handling unstructured data | No | Yes |
| Decision-making | None | Strong |
| Cross-line coordination | Limited | Collaborative |
| Anomaly detection | Reactive | Predictive & proactive |
| Energy optimization | Manual | Autonomous |
| Maintenance | Scheduled | Predictive |
| Scalability | Hard | Exponential |
| Workforce augmentation | Minimal | High |
The data is clear: AI Agents do not replace automation, they transcend it.
How AI Agents Create a Self-Optimizing Factory
Below are the core pillars that define self-optimizing production systems.
1. Autonomous Quality Control
Traditional QC is reactive. AI Agents shift it to continuous, real-time intelligence.
Agents can:
- Analyze visual feeds using vision AI
- Detect microscopic defects
- Compare outputs against digital twin baselines
- Adjust machine parameters without human intervention
Manufacturers using AI-driven QC report:
- Up to 90% reduction in quality escapes
- 30–50% fewer false rejects
2. Predictive and Autonomous Maintenance
AI Agents combine sensor data, machine logs, and historical patterns to:
- Predict failures weeks in advance
- Identify root causes
- Trigger work orders
- Coordinate parts procurement
- Reassign workloads to other machines
This shift cuts downtime by:
- 30–60%
- Extends machine lifespan by 20–40%
- Reduces maintenance costs by 25–35%
3. Dynamic Production Scheduling
Demand fluctuations, machine breakdowns, and supply delays make fixed scheduling obsolete.
AI agents continually:
- Reprioritize jobs
- Reallocate resources
- Coordinate between work cells
- Optimize changeovers
- Account for labor availability
This enables:
- 10–30% throughput improvement
- Faster line recovery during disruptions
4. Autonomous Energy Optimization
Energy is one of manufacturing’s biggest cost drivers.
AI agents optimize:
- Machine run cycles
- Idle time
- Peak-load patterns
- HVAC and utility consumption
Plants adopting energy AI see:
- 8–15% energy savings within 90 days
- 20–30% long-term reductions
5. Supply Chain Synchronization
Agents predict:
- Material shortages
- Lead time variations
- Supplier performance degradation
- Logistics disruptions
They automatically adjust inventory strategies, reorder materials, and re-plan production around constraints.
This minimizes:
- Stockouts
- Line stoppages
- Excess inventory
- Supply chain volatility
The Multi-Agent Factory: A Collaboration Ecosystem
Manufacturing 4.0 is not powered by a single AI agent but a collaborative system of AI agents.
Examples of multi-agent roles:
- Quality Agent: Monitors visual feeds, adjusts tolerances, analyzes rejects.
- Maintenance Agent: Predicts failures, triggers repairs, optimizes spare parts.
- Production Agent: Schedules work orders, manages line balancing.
- Energy Agent: Controls utilities and load balancing.
- Supply Chain Agent: Manages procurement, forecasts shortages.
- Compliance Agent: Ensures SOP adherence, audit trails, safety checks.
Each agent specializes, but they coordinate like a digital operations team creating a unified, self-optimizing ecosystem.
Real Use Cases Driving 20–70% Efficiency Gains
1. Automotive Manufacturing
AI agents detect micro-defects during body fabrication and autonomously recalibrate equipment.
Impact:
- 30% reduction in rework
- 60% drop in defect escapes
2. Electronics Assembly
Vision agents detect solder quality issues and adjust reflow oven settings in real time.
Impact:
- 40% yield improvement
- 25% reduction in scrap
3. Food & Beverage Production
AI agents optimize temperature, conveyor speeds, and dosing processes based on real-time variability.
Impact:
- 15–25% output improvement
- Significant reduction in spoilage
4. Metals & Heavy Industry
AI-driven predictive maintenance extends equipment life and prevents catastrophic failures.
Impact:
- Millions saved in avoided downtime
- 20–40% longer machine life
Technical Architecture for Manufacturing Leaders
Below is a deeper look at the underlying system design that powers Manufacturing 4.0.
AI Models
- LLMs for reasoning
- Vision transformers for QC
- Time-series models for anomaly detection
- RL models for scheduling optimization
Data Fabric
- Industrial IoT
- Edge computing
- OPC-UA integrations
- Real-time data lakes
- Digital twins
Execution Layer
- APIs
- OPC-UA commands
- MES/MOM integrations
- Robotics controllers
- Alerting and control systems
Governance
- Access role models
- Safety protocols
- Human override modes
- Ethical compliance frameworks
This ensures the system is both autonomous and safe.
Why AI Agents Are the Future Operating System of Smart Factories
Traditional automation controls machines. AI Agents control outcomes.
Traditional systems follow rules. AI Agents learn, predict, optimize, and self-correct.
This transition is as significant as the shift from manual workshop production to industrial automation.
Leaders that deploy AI Agents now will build factories that:
- Never stop learning
- Never stop improving
- Never rely on static rules
- Operate with unmatched resilience and precision
A Practical Adoption Roadmap for Manufacturers
1. Identify high-friction workflows
Focus on QC, downtime-heavy assets, or unpredictable scheduling.
2. Deploy a focused AI Agent pilot
Start with a single line or equipment unit.
3. Create a unified data layer
Integrate SCADA, MES, PLC, maintenance, and quality data.
4. Expand to multi-agent collaboration
Add QC, maintenance, and scheduling agents.
5. Integrate digital twins
Enable predictive, simulation-driven optimization.
6. Scale plant-wide
Expand across production lines and global facilities.
Most manufacturers see measurable ROI in 8–14 weeks, with compounding benefits thereafter.
Final Call to Action
Manufacturers are discovering a critical truth: Industry 4.0 will not be defined by automation but by intelligent, autonomous production systems.
AI Agents turn factories into self-optimizing entities capable of outperforming traditional automation in accuracy, adaptability, efficiency, and uptime.
The question is no longer if AI Agents will reshape manufacturing the question is Will you lead the transformation or be disrupted by those who do?
Anand Subramanian
Technology expert and AI enthusiast
Anand Subramanian is a technology expert and AI enthusiast currently leading the marketing function at Intellectyx, a Data, Digital, and AI solutions provider with over a decade of experience working with enterprises and government departments.






























 Link copied!
Link copied!
 Recently Updated News
Recently Updated News