
Occam’s Razor and the Art of Software Design
Last updated: December 20, 2025 Read in fullscreen view
- 10 Apr 2022
 Agile self-organizing teams: What are they? How do they work? 51/535
Agile self-organizing teams: What are they? How do they work? 51/535 - 13 Oct 2021
 Outsourcing Software Development: MVP, Proof of Concept (POC) and Prototyping. Which is better? 40/486
Outsourcing Software Development: MVP, Proof of Concept (POC) and Prototyping. Which is better? 40/486 - 18 Oct 2020
 How to use the "Knowns" and "Unknowns" technique to manage assumptions 38/1089
How to use the "Knowns" and "Unknowns" technique to manage assumptions 38/1089 - 21 May 2022
 "Fail Fast, Fail Often, Fail Forward" is the answer to Agile practices of software success 34/1027
"Fail Fast, Fail Often, Fail Forward" is the answer to Agile practices of software success 34/1027 - 12 Oct 2022
 14 Common Reasons Software Projects Fail (And How To Avoid Them) 31/567
14 Common Reasons Software Projects Fail (And How To Avoid Them) 31/567 - 27 Oct 2020
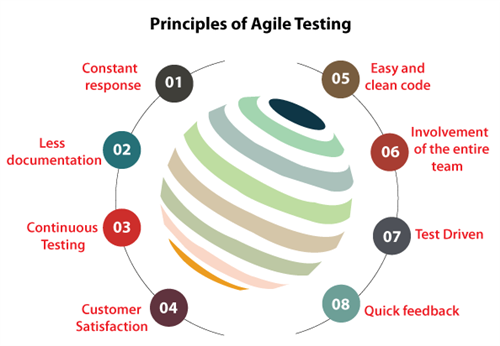
 8 principles of Agile Testing 31/1309
8 principles of Agile Testing 31/1309 - 19 Oct 2021
 Software development life cycles 29/701
Software development life cycles 29/701 - 01 Sep 2022
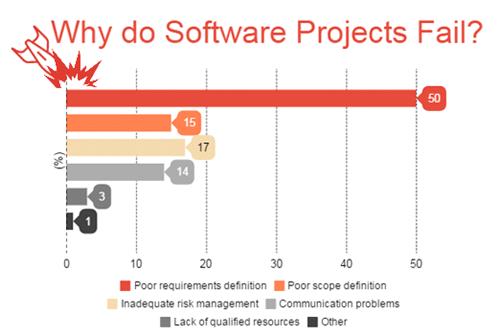
 Facts Chart: Why Do Software Projects Fail? 29/596
Facts Chart: Why Do Software Projects Fail? 29/596 - 01 Oct 2020
 Fail fast, learn faster with Agile methodology 24/1047
Fail fast, learn faster with Agile methodology 24/1047 - 14 Oct 2021
 Advantages and Disadvantages of Time and Material Contract (T&M) 22/864
Advantages and Disadvantages of Time and Material Contract (T&M) 22/864 - 23 Oct 2024
 The Achilles Heel of Secure Software: When “Best-in-Class” Security Still Leads to System Collapse 21/37
The Achilles Heel of Secure Software: When “Best-in-Class” Security Still Leads to System Collapse 21/37 - 12 Jan 2026
 Why YouTube Content Is the New Resume: Building Trust and Expertise Even Without Views 20/33
Why YouTube Content Is the New Resume: Building Trust and Expertise Even Without Views 20/33 - 12 Oct 2020
 The Agile Manifesto - Principle #8 20/496
The Agile Manifesto - Principle #8 20/496 - 13 Dec 2020
 Move fast, fail fast, fail-safe 20/323
Move fast, fail fast, fail-safe 20/323 - 18 Aug 2022
 What are the consequences of poor requirements with software development projects? 20/274
What are the consequences of poor requirements with software development projects? 20/274 - 06 Feb 2021
 Why fail fast and learn fast? 19/450
Why fail fast and learn fast? 19/450 - 16 Apr 2021
 Insightful Business Technology Consulting at TIGO 18/412
Insightful Business Technology Consulting at TIGO 18/412 - 03 Jul 2022
 Manifesto for Agile Software Development 18/276
Manifesto for Agile Software Development 18/276 - 03 Dec 2025
 IT Outsourcing Solutions Explained: What, How, Why, When 18/40
IT Outsourcing Solutions Explained: What, How, Why, When 18/40 - 07 Oct 2025
 Case Study: Using the “Messaging House” Framework to Build a Digital Transformation Roadmap 17/86
Case Study: Using the “Messaging House” Framework to Build a Digital Transformation Roadmap 17/86 - 05 Sep 2023
 The Cold Start Problem: How to Start and Scale Network Effects 17/203
The Cold Start Problem: How to Start and Scale Network Effects 17/203 - 23 Sep 2021
 INFOGRAPHIC: Top 9 Software Outsourcing Mistakes 17/439
INFOGRAPHIC: Top 9 Software Outsourcing Mistakes 17/439 - 04 Oct 2021
 Product Validation: The Key to Developing the Best Product Possible 17/320
Product Validation: The Key to Developing the Best Product Possible 17/320 - 10 Nov 2022
 Poor Code Indicators and How to Improve Your Code? 16/231
Poor Code Indicators and How to Improve Your Code? 16/231 - 01 Mar 2023
 Bug Prioritization - What are the 5 levels of priority? 16/234
Bug Prioritization - What are the 5 levels of priority? 16/234 - 31 Aug 2022
 What are the best practices for software contract negotiations? 16/260
What are the best practices for software contract negotiations? 16/260 - 19 Sep 2025
 The Paradoxes of Scrum Events: When You “Follow the Ritual” but Lose the Value 16/31
The Paradoxes of Scrum Events: When You “Follow the Ritual” but Lose the Value 16/31 - 05 Mar 2021
 How do you minimize risks when you outsource software development? 15/335
How do you minimize risks when you outsource software development? 15/335 - 19 Oct 2021
 Is gold plating good or bad in project management? 15/816
Is gold plating good or bad in project management? 15/816 - 19 Apr 2021
 7 Most Common Time-Wasters For Software Development 14/556
7 Most Common Time-Wasters For Software Development 14/556 - 07 Aug 2022
 Things to Consider When Choosing a Technology Partner 14/283
Things to Consider When Choosing a Technology Partner 14/283 - 08 Nov 2022
 4 tips for meeting tough deadlines when outsourcing projects to software vendor 14/291
4 tips for meeting tough deadlines when outsourcing projects to software vendor 14/291 - 10 Jul 2025
 Building AI-Driven Knowledge Graphs from Unstructured Data 14/162
Building AI-Driven Knowledge Graphs from Unstructured Data 14/162 - 12 May 2024
 The Pros and Cons of the Creator Economy in the Age of AI: Opportunities, Challenges, and the Gray Zone with the Gig Economy 14/270
The Pros and Cons of the Creator Economy in the Age of AI: Opportunities, Challenges, and the Gray Zone with the Gig Economy 14/270 - 07 Jul 2021
 The 5 Levels of IT Help Desk Support 13/448
The 5 Levels of IT Help Desk Support 13/448 - 28 Jul 2022
 POC, Prototypes, Pilots and MVP: What Are the Differences? 13/697
POC, Prototypes, Pilots and MVP: What Are the Differences? 13/697 - 10 Apr 2021
 RFP vs POC: Why the proof of concept is replacing the request for proposal 12/322
RFP vs POC: Why the proof of concept is replacing the request for proposal 12/322 - 28 Oct 2022
 Build Operate Transfer (B.O.T) Model in Software Outsourcing 12/405
Build Operate Transfer (B.O.T) Model in Software Outsourcing 12/405 - 31 Oct 2021
 Tips to Fail Fast With Outsourcing 12/392
Tips to Fail Fast With Outsourcing 12/392 - 17 Jun 2021
 What is IT-business alignment? 12/374
What is IT-business alignment? 12/374 - 08 Oct 2022
 KPI - The New Leadership 12/602
KPI - The New Leadership 12/602 - 07 Oct 2020
 How To Manage Expectations at Work (and Why It's Important) 11/306
How To Manage Expectations at Work (and Why It's Important) 11/306 - 06 Mar 2021
 4 things you need to do before getting an accurate quote for your software development 11/679
4 things you need to do before getting an accurate quote for your software development 11/679 - 09 Oct 2022
 Key Advantages and Disadvantages of Agile Methodology 11/697
Key Advantages and Disadvantages of Agile Methodology 11/697 - 16 Feb 2021
 Choose Outsourcing for Your Non Disclosure Agreement (NDA) 11/173
Choose Outsourcing for Your Non Disclosure Agreement (NDA) 11/173 - 04 Oct 2022
 Which ERP implementation strategy is right for your business? 11/313
Which ERP implementation strategy is right for your business? 11/313 - 01 Mar 2022
 Why Does Scrum Fail in Large Companies? 11/265
Why Does Scrum Fail in Large Companies? 11/265 - 10 Dec 2023
 Pain points of User Acceptance Testing (UAT) 11/452
Pain points of User Acceptance Testing (UAT) 11/452 - 12 Dec 2021
 Zero Sum Games Agile vs. Waterfall Project Management Methods 10/409
Zero Sum Games Agile vs. Waterfall Project Management Methods 10/409 - 28 Dec 2021
 8 types of pricing models in software development outsourcing 10/437
8 types of pricing models in software development outsourcing 10/437 - 03 Nov 2022
 Top questions and answers you must know before ask for software outsourcing 10/291
Top questions and answers you must know before ask for software outsourcing 10/291 - 17 Feb 2022
 Prioritizing Software Requirements with Kano Analysis 10/304
Prioritizing Software Requirements with Kano Analysis 10/304 - 18 Jul 2021
 How To Ramp Up An Offshore Software Development Team Quickly 9/593
How To Ramp Up An Offshore Software Development Team Quickly 9/593 - 20 Nov 2022
 Agile working method in software and football 9/344
Agile working method in software and football 9/344 - 05 Jan 2024
 Easy ASANA tips & tricks for you and your team 9/200
Easy ASANA tips & tricks for you and your team 9/200 - 11 Jan 2024
 What are the Benefits and Limitations of Augmented Intelligence? 9/477
What are the Benefits and Limitations of Augmented Intelligence? 9/477 - 12 Mar 2024
 How do you create FOMO in software prospects? 9/167
How do you create FOMO in software prospects? 9/167 - 01 Dec 2022
 Difference between Set-based development and Point-based development 8/346
Difference between Set-based development and Point-based development 8/346 - 09 Jan 2022
 How to Bridge the Gap Between Business and IT? 8/178
How to Bridge the Gap Between Business and IT? 8/178 - 02 Nov 2022
 Frequently Asked Questions about Agile and Scrum 8/399
Frequently Asked Questions about Agile and Scrum 8/399 - 09 Mar 2022
 Consultant Implementation Pricing 8/213
Consultant Implementation Pricing 8/213 - 21 Oct 2022
 Virtual meeting - How does TIGO save cost, reduce complexity and improve quality by remote communication? 8/191
Virtual meeting - How does TIGO save cost, reduce complexity and improve quality by remote communication? 8/191 - 16 Jul 2022
 What are disadvantages of Agile Methodology? How to mitigate the disadvantages ? 7/376
What are disadvantages of Agile Methodology? How to mitigate the disadvantages ? 7/376 - 01 Jun 2022
 How Your Agile Development Team is Just Like a Football Team? 7/224
How Your Agile Development Team is Just Like a Football Team? 7/224 - 01 Mar 2023
 How do you deal with disputes and conflicts that may arise during a software consulting project? 7/165
How do you deal with disputes and conflicts that may arise during a software consulting project? 7/165 - 06 Mar 2024
 [SemRush] What Are LSI Keywords & Why They Don‘t Matter 7/176
[SemRush] What Are LSI Keywords & Why They Don‘t Matter 7/176 - 12 Aug 2024
 Understanding Google Analytics in Mumbai: A Beginner's Guide 6/99
Understanding Google Analytics in Mumbai: A Beginner's Guide 6/99 - 14 Mar 2024
 Why should you opt for software localization from a professional agency? 6/140
Why should you opt for software localization from a professional agency? 6/140 - 06 Nov 2019
 How to Access Software Project Size? 6/249
How to Access Software Project Size? 6/249 - 10 Oct 2022
 Should Your Business Go Agile? (Infographic) 6/128
Should Your Business Go Agile? (Infographic) 6/128 - 07 Oct 2022
 Digital Transformation: Become a Technology Powerhouse 6/244
Digital Transformation: Become a Technology Powerhouse 6/244 - 01 May 2023
 CTO Interview Questions 5/329
CTO Interview Questions 5/329 - 01 Dec 2023
 Laws of Project Management 5/302
Laws of Project Management 5/302 - 26 Dec 2023
 Improving Meeting Effectiveness Through the Six Thinking Hats 5/253
Improving Meeting Effectiveness Through the Six Thinking Hats 5/253 - 09 Feb 2023
 The Challenge of Fixed-Bid Software Projects 5/213
The Challenge of Fixed-Bid Software Projects 5/213 - 20 Nov 2022
 Software Requirements Are A Communication Problem 5/244
Software Requirements Are A Communication Problem 5/244 - 28 Nov 2023
 Scrum Team Failure — Scrum Anti-Patterns Taxonomy 5/253
Scrum Team Failure — Scrum Anti-Patterns Taxonomy 5/253 - 30 Oct 2022
 How Much Does MVP Development Cost in 2023? 5/240
How Much Does MVP Development Cost in 2023? 5/240 - 12 Apr 2025
 How to Ask Powerful Questions Like Socrates 5/34
How to Ask Powerful Questions Like Socrates 5/34 - 23 May 2024
 Mastering AI: Sharpening the Axe in the Digital Age 5/245
Mastering AI: Sharpening the Axe in the Digital Age 5/245 - 01 May 2024
 Warren Buffett’s Golden Rule for Digital Transformation: Avoiding Tech Overload 3/205
Warren Buffett’s Golden Rule for Digital Transformation: Avoiding Tech Overload 3/205 - 17 Mar 2025
 IT Consultants in Digital Transformation 2/83
IT Consultants in Digital Transformation 2/83
Occam's Razor, a 14th-century philosophy, emphasizes simplicity over complexity. It suggests that the simplest solution is often the best, but this is often interpreted as the "fewest assumptions" or Principle of Parsimony. The principle is based on the idea that entities should not be multiplied beyond necessity. This principle is often used in software design, where the simplest solution is often the best.
The premise of Occam’s razor is that “entities should not be multiplied without necessity”. It emphasizes choosing the solution with the fewest assumptions when faced with competing hypotheses concerning the same prediction; nevertheless, it should be noted that this is not a method of selecting amongst hypotheses that make different predictions.
It is often mistaken to advocate simplicity, but has a more nuanced recommendation, which is described by the quote “Everything should be made as simple as possible, but no simpler.”. This idea, which goes, "It is vain to do with more what can be done with fewer".
In software design, it is crucial to question the validity of assumptions and ensure that everything is done in support of project objectives. By embodying Occam's Razor and doing less, developers can improve their productivity and overall productivity.
80% of the functionality built into software application is either never, or rarely used.
Scrum and Agile methods in software development focus on delivering value to end users. This approach ensures constant assessment and re-prioritization of features and functionality, leading to stakeholder satisfaction earlier in the development process. However, this approach is not enough.
In the world of predictive models, one needs to maintain a balance between model complexity and error, that would be a sweet spot between over-generalization and over-specialization.
Software solutions are increasingly complex due to the increasing requirements of application solutions. Complexity introduces uncertainty and risk, increasing the probability of failure. Plurality, which adds entities to support conclusions, multiplies the complexity of the system. The number of entities in a software system increases as the number of entities increases, but it is crucial to ensure that changes in any one entity will not impact any other. Additionally, the system's complexity increases with the number of assumptions, which represent assumptions in Occam's view. The more assumptions a system has, the more complex it becomes, and thus the higher the probability of failure.
Key Points
Software Development and Occam's Principles
- The principles espoused by Occam are not enough to address the increasing complexity of software solutions.
- Complexity introduces uncertainty and risk, increasing the probability of failure.
- Plurality in software adds complexity, not just adding entities.
- The complexity of the system increases as the number of entities increases.
- The complexity of the system is not in the dots, but the number of lines connecting them.
The complexity of the system increases with the number of entities added. - The "what if's" represent assumptions in Occam's view, which increase with the number of entities added.
- Scrum and Agile Methods in software development focus on delivering value to end users, reducing the need for technology.
- 80% of the functionality in software applications is either never used or rarely used.
- Continuous assessment and re-prioritization of features and functionality ensures stakeholder satisfaction.
Continue reading at michaellant.com
| About the Author | Michael Lant | IT Consultant | MICHAEL LANT: Software Archictecture, Development, Agile Methods and the Intersection of People Process and Technology. I am an independent consultant who has been leading software teams, designing, building and delivering software for nearly three decades. It’s still as exciting and enjoyable for me today as at was when I wrote my very first Hello World program and saw it spring to life in front of me. |




























 Link copied!
Link copied!
 Recently Updated News
Recently Updated News