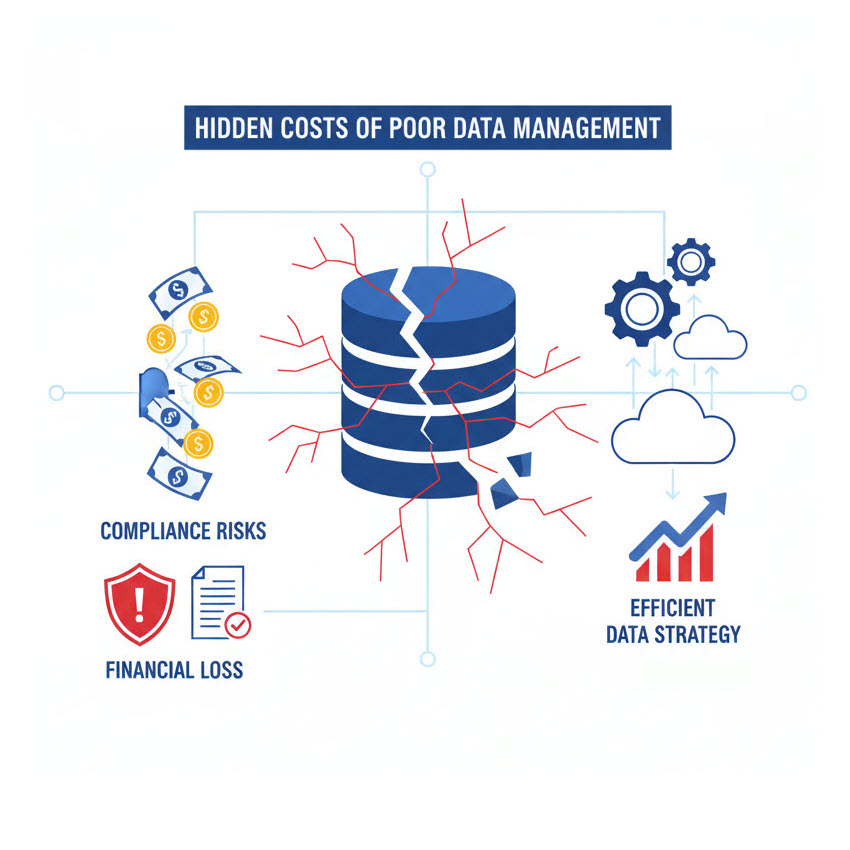
The Hidden Costs of Poor Data Management and How to Stop Them
Last updated: November 07, 2025 Read in fullscreen view
- 01 May 2023
 Understanding Business as Usual (BAU) and How to Transition 52/930
Understanding Business as Usual (BAU) and How to Transition 52/930 - 18 Oct 2020
 How to use the "Knowns" and "Unknowns" technique to manage assumptions 38/1089
How to use the "Knowns" and "Unknowns" technique to manage assumptions 38/1089 - 21 Nov 2025
 The Pressure of Short-Term Funding on Small-Budget IT Projects 25/35
The Pressure of Short-Term Funding on Small-Budget IT Projects 25/35 - 01 Oct 2020
 Fail fast, learn faster with Agile methodology 24/1047
Fail fast, learn faster with Agile methodology 24/1047 - 28 Jul 2025
 Data Modernization for SMBs: Small Steps, Big Impact 24/165
Data Modernization for SMBs: Small Steps, Big Impact 24/165 - 21 Sep 2023
 Abraham Wald and the Missing Bullet Holes 22/666
Abraham Wald and the Missing Bullet Holes 22/666 - 14 Oct 2021
 Advantages and Disadvantages of Time and Material Contract (T&M) 22/864
Advantages and Disadvantages of Time and Material Contract (T&M) 22/864 - 18 Dec 2025
 AI: Act Now or Wait Until You’re “Ready”? 22/42
AI: Act Now or Wait Until You’re “Ready”? 22/42 - 13 Dec 2020
 Move fast, fail fast, fail-safe 20/323
Move fast, fail fast, fail-safe 20/323 - 18 Aug 2022
 What are the consequences of poor requirements with software development projects? 20/274
What are the consequences of poor requirements with software development projects? 20/274 - 06 Feb 2021
 Why fail fast and learn fast? 19/450
Why fail fast and learn fast? 19/450 - 17 Mar 2025
 Integrating Salesforce with Yardi: A Guide to Achieving Success in Real Estate Business 19/202
Integrating Salesforce with Yardi: A Guide to Achieving Success in Real Estate Business 19/202 - 01 Mar 2023
 Bug Prioritization - What are the 5 levels of priority? 17/235
Bug Prioritization - What are the 5 levels of priority? 17/235 - 23 Sep 2021
 INFOGRAPHIC: Top 9 Software Outsourcing Mistakes 17/439
INFOGRAPHIC: Top 9 Software Outsourcing Mistakes 17/439 - 10 Nov 2022
 Poor Code Indicators and How to Improve Your Code? 16/231
Poor Code Indicators and How to Improve Your Code? 16/231 - 19 Oct 2021
 Is gold plating good or bad in project management? 15/816
Is gold plating good or bad in project management? 15/816 - 08 May 2024
 Time Unlocked: Mastering the Pomodoro Technique Against Parkinson's Law 15/235
Time Unlocked: Mastering the Pomodoro Technique Against Parkinson's Law 15/235 - 26 Sep 2024
 Successful Project Management Techniques You Need to Look Out For 14/401
Successful Project Management Techniques You Need to Look Out For 14/401 - 19 Apr 2021
 7 Most Common Time-Wasters For Software Development 14/556
7 Most Common Time-Wasters For Software Development 14/556 - 08 Aug 2022
 Difference between Power BI and Datazen 13/329
Difference between Power BI and Datazen 13/329 - 08 Oct 2022
 KPI - The New Leadership 12/602
KPI - The New Leadership 12/602 - 31 Oct 2021
 Tips to Fail Fast With Outsourcing 12/392
Tips to Fail Fast With Outsourcing 12/392 - 10 Dec 2023
 Pain points of User Acceptance Testing (UAT) 11/452
Pain points of User Acceptance Testing (UAT) 11/452 - 28 Dec 2021
 8 types of pricing models in software development outsourcing 10/437
8 types of pricing models in software development outsourcing 10/437 - 17 Feb 2022
 Prioritizing Software Requirements with Kano Analysis 10/304
Prioritizing Software Requirements with Kano Analysis 10/304 - 03 May 2024
 The Iceberg of Ignorance 10/403
The Iceberg of Ignorance 10/403 - 05 Sep 2024
 The Inverted Approach: A Guide to Identifying Software Risks with Reverse Brainstorming 9/255
The Inverted Approach: A Guide to Identifying Software Risks with Reverse Brainstorming 9/255 - 09 Sep 2024
 How AI Rewriting Can Improve Your Content’s SEO Performance 9/188
How AI Rewriting Can Improve Your Content’s SEO Performance 9/188 - 05 Jan 2024
 Easy ASANA tips & tricks for you and your team 9/200
Easy ASANA tips & tricks for you and your team 9/200 - 11 Jan 2024
 What are the Benefits and Limitations of Augmented Intelligence? 9/477
What are the Benefits and Limitations of Augmented Intelligence? 9/477 - 12 Mar 2024
 How do you create FOMO in software prospects? 9/167
How do you create FOMO in software prospects? 9/167 - 05 Oct 2021
 Shiny Object Syndrome: Why Your Business Isn't "Going Digital" 7/350
Shiny Object Syndrome: Why Your Business Isn't "Going Digital" 7/350 - 14 Mar 2024
 Why should you opt for software localization from a professional agency? 6/140
Why should you opt for software localization from a professional agency? 6/140 - 26 Dec 2023
 Improving Meeting Effectiveness Through the Six Thinking Hats 6/254
Improving Meeting Effectiveness Through the Six Thinking Hats 6/254 - 06 Nov 2019
 How to Access Software Project Size? 6/249
How to Access Software Project Size? 6/249 - 15 Aug 2025
 Quantum Technology: Global Challenges and Opportunities for Innovators 4/100
Quantum Technology: Global Challenges and Opportunities for Innovators 4/100 - 12 Sep 2024
 Be Water, My Friend: Fluidity, Flow & Going With the Flow 3/169
Be Water, My Friend: Fluidity, Flow & Going With the Flow 3/169 - 19 Apr 2024
 What is Skills-Based Approach & Why Does it Matter? 3/134
What is Skills-Based Approach & Why Does it Matter? 3/134
| About the Author | Anand Subramanian | Technology expert and AI enthusiast |
Anand Subramanian is a technology expert and AI enthusiast currently leading the marketing function at Intellectyx, a Data, Digital, and AI solutions provider with over a decade of experience working with enterprises and government departments. |
In today’s data-driven economy, poor data management is not just an inconvenience. It is a silent cost center that compounds over time, draining efficiency, increasing risk, and slowing down innovation. For growing enterprises that are scaling operations, entering new markets, and investing in digital transformation, data mismanagement can be devastating.
The biggest problem? The damage is often invisible until it’s too late. Whether caused by siloed systems, unclear ownership, or weak governance, the impact accumulates quietly. Over time, these cracks in your data strategy erode performance, disrupt decision-making, and weaken customer trust.
This article uncovers the hidden costs of poor data management with real-world examples and actionable strategies to avoid them.
The Growth Challenge: When Data Outpaces Strategy
As enterprises scale, the volume and variety of data grows at lightning speed. CRMs, analytics tools, IoT devices, and customer support systems all generate data points daily. Collecting data, however, is not the same as managing it effectively.
If your governance model does not evolve alongside this growth, the gap widens. According to Gartner, poor data quality costs organizations an average of $12.9 million annually, a number that skyrockets in businesses where critical decisions depend on data.
Hidden Cost 1: Decision-Making Paralysis and Mistrust
When data lives in disconnected systems and reports conflict, decision-makers lose confidence. They hesitate or make decisions based on incomplete insights, putting growth at risk.
Real-World Example: Target’s Canadian Expansion Failure (2015)
Target’s entry into Canada is a textbook case. Their inventory and supply chain systems were riddled with incorrect data, product dimensions, weights, and prices were wrong. The result? Empty shelves, frustrated customers, and a $2 billion loss. Within two years, all 133 Canadian stores were closed.
Hidden Cost 2: Operational Inefficiency and Redundancy
Disconnected systems and manual reconciliation drain resources. Teams waste hours cleaning data and duplicating work instead of focusing on innovation.
Real-World Example: NHS Digital’s COVID-19 Reporting Delay
In 2020, the UK’s COVID-19 response was delayed because Public Health England relied on outdated Excel systems. A file format limitation caused nearly 16,000 COVID-19 test results to go missing. The fallout? Delayed contact tracing, poor public health planning, and loss of trust.
Hidden Cost 3: Regulatory and Legal Risks
Privacy laws such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA impose strict requirements for data handling. Weak governance can lead to massive fines and reputational harm.
Real-World Example: Equifax Data Breach (2017)
Due to poor patch management and lack of security controls, Equifax exposed sensitive data of 147 million Americans. The company paid $700 million in settlements, one of the largest penalties for a data breach.
Hidden Cost 4: Loss of Customer Trust and Retention
Outdated or inconsistent customer data ruins personalization and creates broken experiences. Customers leave when they feel misunderstood or underserved.
Real-World Example: Amazon’s Buy Box Algorithm Scrutiny
Even Amazon faced criticism in 2020 over its Buy Box algorithm, which allegedly favored certain sellers due to flawed input data. The backlash fueled antitrust concerns and damaged trust among small businesses.
Hidden Cost 5: Stifled Innovation and Slow Product Development
Without clean and accessible data, innovation stalls. Testing new models or rolling out customer-driven features becomes nearly impossible.
Real-World Example: Sears’ Modernization Struggles
Sears’ outdated IT systems limited their ability to track trends or leverage predictive analytics. Competitors embraced AI and personalization while Sears was stuck with spreadsheets. The result? Lost relevance and eventual bankruptcy.
Why These Costs Go Unnoticed
These issues rarely trigger alarms until they explode into a crisis because:
- The pain is distributed across multiple teams, marketing, finance, legal, engineering, so no one owns the problem.
- The impact builds slowly over time.
- Businesses often patch symptoms with more tools instead of fixing root causes.
On the surface, the system looks functional, but beneath it, the cracks are widening.
Practical Steps to Avoid These Hidden Costs
If you want to future-proof your enterprise and eliminate the hidden costs of poor data management, start with these strategic actions:
1. Define a Data Ownership Model
Data governance starts with clear accountability. Assign domain-specific data stewards who take responsibility for maintaining data quality, documentation, and compliance within their areas. These stewards act as the bridge between business teams and IT, ensuring that every dataset has a clear owner and that standards are consistently applied.
2. Implement Automated Data Quality Checks
Manual checks are not scalable in a modern data ecosystem. Automated data quality monitoring detects anomalies, missing values, duplicates, and format inconsistencies before they disrupt business processes.
3. Adopt a Modern Data Stack
Legacy systems often struggle with the scale and complexity of enterprise data. Moving to a modern, cloud-native architecture helps you manage high-volume, high-velocity data efficiently.
What This Means:
- Use platforms like Snowflake, Databricks, or Google BigQuery for elastic scaling and real-time analytics.
- Separate compute and storage to optimize costs.
- Enable data lakehouse architecture for both structured and unstructured data.
4. Build Privacy into Design
Data privacy cannot be an afterthought. As regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA become more stringent, compliance must be built into your architecture and workflows from day one.
Key Practices:
- Implement encryption at rest and in transit.
- Use data masking for sensitive fields in non-production environments.
- Maintain detailed audit logs to track access and changes.
5. Promote Data Literacy Across Teams
Even the most advanced technology is useless if your teams cannot interpret or trust the data. Building a culture of data literacy ensures better decision-making and ownership.
Action Tip:
- Conduct regular training sessions on reading dashboards, validating insights, and understanding data lineage.
- Provide self-service BI tools like Looker or Power BI so teams can explore data without IT bottlenecks.
- Introduce data storytelling workshops to help employees communicate insights effectively.
6. Establish Strong Metadata Management
Without proper metadata, data becomes a black box. Metadata provides context such as source, lineage, and usage policies.
7. Create a Data Observability Framework
Data observability is like DevOps for your data pipelines. It focuses on monitoring pipeline health, data freshness, and anomaly detection in real-time.
8. Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Data breaches and compliance failures often happen due to uncontrolled access. Implementing RBAC ensures users only access the data necessary for their role.
9. Build a Centralized Data Governance Council
Governance needs leadership. Form a council comprising stakeholders from IT, business, security, and compliance teams. This group sets policies, monitors adherence, and reviews exceptions.
10. Measure and Monitor Data Value Continuously
What gets measured gets managed. Define KPIs for data health, usage, and ROI. Examples include:
- Data Quality Index: Tracks accuracy, completeness, and timeliness.
- Data Usage Metrics: Monitors adoption across teams.
- Compliance Score: Evaluates adherence to privacy regulations.
The Bottom Line
Data is no longer just a record of transactions. It is the fuel for growth, innovation, and competitive advantage. But only if it is trusted, accurate, and governed.
The hidden costs of poor data management, lost revenue, legal risks, operational delays, and broken trust are avoidable. Real-world failures like Target and Equifax prove that no company is too big to fall victim. On the other hand, companies that invest in strong data foundations create a lasting competitive edge.
For growing enterprises, the message is clear: manage your data like a strategic asset before it becomes your biggest liability.
Anand Subramanian
Technology expert and AI enthusiast
Anand Subramanian is a technology expert and AI enthusiast currently leading the marketing function at Intellectyx, a Data, Digital, and AI solutions provider with over a decade of experience working with enterprises and government departments.



























 Link copied!
Link copied!
 Recently Updated News
Recently Updated News