The Three Pillars of Empiricism in Scrum
Last updated: December 20, 2025 Read in fullscreen view
- 10 Apr 2022
 Agile self-organizing teams: What are they? How do they work? 51/535
Agile self-organizing teams: What are they? How do they work? 51/535 - 13 Oct 2021
 Outsourcing Software Development: MVP, Proof of Concept (POC) and Prototyping. Which is better? 40/486
Outsourcing Software Development: MVP, Proof of Concept (POC) and Prototyping. Which is better? 40/486 - 18 Oct 2020
 How to use the "Knowns" and "Unknowns" technique to manage assumptions 38/1089
How to use the "Knowns" and "Unknowns" technique to manage assumptions 38/1089 - 21 May 2022
 "Fail Fast, Fail Often, Fail Forward" is the answer to Agile practices of software success 34/1027
"Fail Fast, Fail Often, Fail Forward" is the answer to Agile practices of software success 34/1027 - 12 Oct 2022
 14 Common Reasons Software Projects Fail (And How To Avoid Them) 31/567
14 Common Reasons Software Projects Fail (And How To Avoid Them) 31/567 - 27 Oct 2020
 8 principles of Agile Testing 31/1309
8 principles of Agile Testing 31/1309 - 19 Oct 2021
 Software development life cycles 29/701
Software development life cycles 29/701 - 01 Oct 2020
 Fail fast, learn faster with Agile methodology 24/1047
Fail fast, learn faster with Agile methodology 24/1047 - 15 Jan 2026
 ITIL vs PMP: What’s the Difference and Which One Should You Choose? 23/32
ITIL vs PMP: What’s the Difference and Which One Should You Choose? 23/32 - 14 Oct 2021
 Advantages and Disadvantages of Time and Material Contract (T&M) 22/864
Advantages and Disadvantages of Time and Material Contract (T&M) 22/864 - 25 Sep 2018
 Applying Cognitive Linguistics to Multi-Stakeholder Communication in IT Projects 21/28
Applying Cognitive Linguistics to Multi-Stakeholder Communication in IT Projects 21/28 - 18 Aug 2022
 What are the consequences of poor requirements with software development projects? 20/274
What are the consequences of poor requirements with software development projects? 20/274 - 12 Oct 2020
 The Agile Manifesto - Principle #8 20/496
The Agile Manifesto - Principle #8 20/496 - 13 Dec 2020
 Move fast, fail fast, fail-safe 20/323
Move fast, fail fast, fail-safe 20/323 - 06 Feb 2021
 Why fail fast and learn fast? 19/450
Why fail fast and learn fast? 19/450 - 03 Jul 2022
 Manifesto for Agile Software Development 18/276
Manifesto for Agile Software Development 18/276 - 07 Oct 2025
 Case Study: Using the “Messaging House” Framework to Build a Digital Transformation Roadmap 17/86
Case Study: Using the “Messaging House” Framework to Build a Digital Transformation Roadmap 17/86 - 05 Sep 2023
 The Cold Start Problem: How to Start and Scale Network Effects 17/203
The Cold Start Problem: How to Start and Scale Network Effects 17/203 - 23 Sep 2021
 INFOGRAPHIC: Top 9 Software Outsourcing Mistakes 17/439
INFOGRAPHIC: Top 9 Software Outsourcing Mistakes 17/439 - 04 Oct 2021
 Product Validation: The Key to Developing the Best Product Possible 17/320
Product Validation: The Key to Developing the Best Product Possible 17/320 - 05 Mar 2021
 How do you minimize risks when you outsource software development? 16/336
How do you minimize risks when you outsource software development? 16/336 - 31 Aug 2022
 What are the best practices for software contract negotiations? 16/260
What are the best practices for software contract negotiations? 16/260 - 10 Nov 2022
 Poor Code Indicators and How to Improve Your Code? 16/231
Poor Code Indicators and How to Improve Your Code? 16/231 - 01 Mar 2023
 Bug Prioritization - What are the 5 levels of priority? 16/234
Bug Prioritization - What are the 5 levels of priority? 16/234 - 19 Oct 2021
 Is gold plating good or bad in project management? 15/816
Is gold plating good or bad in project management? 15/816 - 19 Apr 2021
 7 Most Common Time-Wasters For Software Development 14/556
7 Most Common Time-Wasters For Software Development 14/556 - 28 Jul 2022
 POC, Prototypes, Pilots and MVP: What Are the Differences? 13/697
POC, Prototypes, Pilots and MVP: What Are the Differences? 13/697 - 08 Oct 2022
 KPI - The New Leadership 12/602
KPI - The New Leadership 12/602 - 28 Oct 2022
 Build Operate Transfer (B.O.T) Model in Software Outsourcing 12/405
Build Operate Transfer (B.O.T) Model in Software Outsourcing 12/405 - 31 Oct 2021
 Tips to Fail Fast With Outsourcing 12/392
Tips to Fail Fast With Outsourcing 12/392 - 17 Jun 2021
 What is IT-business alignment? 12/374
What is IT-business alignment? 12/374 - 09 Oct 2022
 Key Advantages and Disadvantages of Agile Methodology 11/697
Key Advantages and Disadvantages of Agile Methodology 11/697 - 07 Oct 2020
 How To Manage Expectations at Work (and Why It's Important) 11/306
How To Manage Expectations at Work (and Why It's Important) 11/306 - 04 Oct 2022
 Which ERP implementation strategy is right for your business? 11/313
Which ERP implementation strategy is right for your business? 11/313 - 01 Mar 2022
 Why Does Scrum Fail in Large Companies? 11/265
Why Does Scrum Fail in Large Companies? 11/265 - 10 Dec 2023
 Pain points of User Acceptance Testing (UAT) 11/452
Pain points of User Acceptance Testing (UAT) 11/452 - 12 Dec 2021
 Zero Sum Games Agile vs. Waterfall Project Management Methods 10/409
Zero Sum Games Agile vs. Waterfall Project Management Methods 10/409 - 28 Dec 2021
 8 types of pricing models in software development outsourcing 10/437
8 types of pricing models in software development outsourcing 10/437 - 17 Feb 2022
 Prioritizing Software Requirements with Kano Analysis 10/304
Prioritizing Software Requirements with Kano Analysis 10/304 - 20 Nov 2022
 Agile working method in software and football 9/344
Agile working method in software and football 9/344 - 18 Jul 2021
 How To Ramp Up An Offshore Software Development Team Quickly 9/593
How To Ramp Up An Offshore Software Development Team Quickly 9/593 - 05 Jan 2024
 Easy ASANA tips & tricks for you and your team 9/200
Easy ASANA tips & tricks for you and your team 9/200 - 11 Jan 2024
 What are the Benefits and Limitations of Augmented Intelligence? 9/477
What are the Benefits and Limitations of Augmented Intelligence? 9/477 - 12 Mar 2024
 How do you create FOMO in software prospects? 9/167
How do you create FOMO in software prospects? 9/167 - 09 Sep 2022
 Debunking 50+ Agile Scrum Interview Questions 8/436
Debunking 50+ Agile Scrum Interview Questions 8/436 - 01 Dec 2022
 Difference between Set-based development and Point-based development 8/346
Difference between Set-based development and Point-based development 8/346 - 07 Sep 2022
 The Adaptive Scrum: Why Modified Agile Model? 8/322
The Adaptive Scrum: Why Modified Agile Model? 8/322 - 21 Oct 2022
 Virtual meeting - How does TIGO save cost, reduce complexity and improve quality by remote communication? 8/191
Virtual meeting - How does TIGO save cost, reduce complexity and improve quality by remote communication? 8/191 - 02 Nov 2022
 Frequently Asked Questions about Agile and Scrum 8/399
Frequently Asked Questions about Agile and Scrum 8/399 - 16 Jul 2022
 What are disadvantages of Agile Methodology? How to mitigate the disadvantages ? 7/376
What are disadvantages of Agile Methodology? How to mitigate the disadvantages ? 7/376 - 01 Jun 2022
 How Your Agile Development Team is Just Like a Football Team? 7/224
How Your Agile Development Team is Just Like a Football Team? 7/224 - 06 Mar 2024
 [SemRush] What Are LSI Keywords & Why They Don‘t Matter 7/176
[SemRush] What Are LSI Keywords & Why They Don‘t Matter 7/176 - 26 Dec 2023
 Improving Meeting Effectiveness Through the Six Thinking Hats 6/254
Improving Meeting Effectiveness Through the Six Thinking Hats 6/254 - 12 Aug 2024
 Understanding Google Analytics in Mumbai: A Beginner's Guide 6/99
Understanding Google Analytics in Mumbai: A Beginner's Guide 6/99 - 14 Mar 2024
 Why should you opt for software localization from a professional agency? 6/140
Why should you opt for software localization from a professional agency? 6/140 - 10 Oct 2022
 Should Your Business Go Agile? (Infographic) 6/128
Should Your Business Go Agile? (Infographic) 6/128 - 06 Nov 2019
 How to Access Software Project Size? 6/249
How to Access Software Project Size? 6/249 - 01 Dec 2023
 Laws of Project Management 5/302
Laws of Project Management 5/302 - 28 Nov 2023
 Scrum Team Failure — Scrum Anti-Patterns Taxonomy 5/253
Scrum Team Failure — Scrum Anti-Patterns Taxonomy 5/253 - 06 Sep 2021
 Scrum Flexibility: Navigating the Boundaries of Agile Modification 5/319
Scrum Flexibility: Navigating the Boundaries of Agile Modification 5/319 - 01 May 2024
 Warren Buffett’s Golden Rule for Digital Transformation: Avoiding Tech Overload 3/205
Warren Buffett’s Golden Rule for Digital Transformation: Avoiding Tech Overload 3/205 - 06 Mar 2024
 Most Common Software Development Methodologies 1/157
Most Common Software Development Methodologies 1/157
means working in a fact-based, experience-based, and evidence-based manner. Scrum implements an empirical process where progress is based on observations of reality, not fictitious plans. Scrum also places great emphasis on mind-set and cultural shift to achieve business and organizational Agility.
“Scrum is founded on empiricism and lean thinking. Empiricism asserts that knowledge comes from experience and making decisions based on what is observed. Lean thinking reduces waste and focuses on the essentials.”
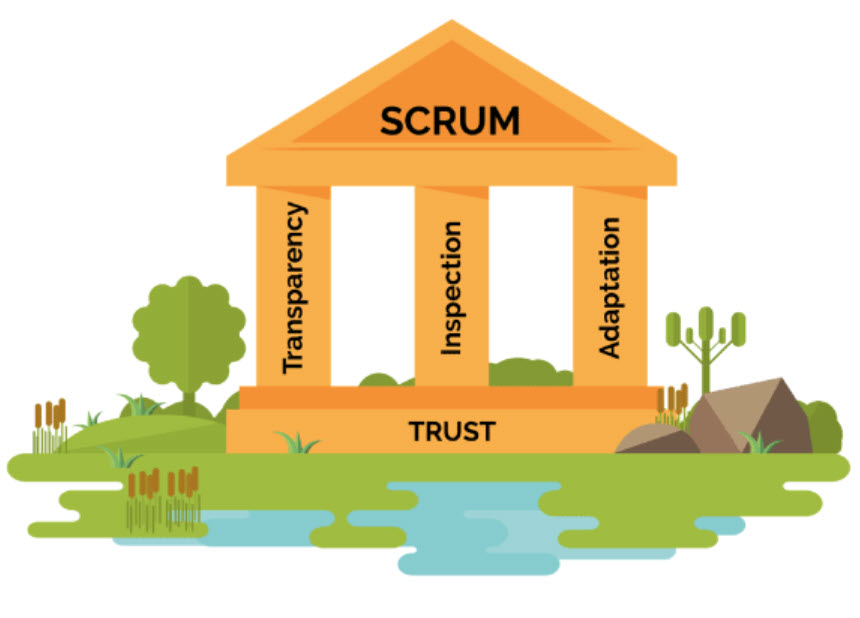
The three pillars of empiricism
The three pillars of empiricism are as follows:
-
Transparency
This means presenting the facts as is. All people involved - the customer, the CEO, individual contributors - are transparent in their day-to-day dealings with others. They all trust each other, and they have the courage to keep each other abreast of good news as well as bad news. Everyone strives and collectively collaborates for the common organizational objective, and no one has any hidden agenda.
-
Inspection
Inspection in this context is not an inspection by an inspector or an auditor but an inspection by everyone on the Scrum Team. The inspection can be done for the product, processes, people aspects, practices, and continuous improvements. For example, the team openly and transparently shows the product at the end of each Sprint to the customer in order to gather valuable feedback. If the customer changes the requirements during inspection, the team does not complain but rather adapts by using this as an opportunity to collaborate with the customer to clarify the requirements and test out the new hypothesis.
“Transparency enables inspection. Inspection without transparency is misleading and wasteful.”
-
Adaptation
Adaptation in this context is about continuous improvement, the ability to adapt based on the results of the inspection. Everyone in the organization must ask this question regularly: Are we better off than yesterday? For profit-based organizations, the value is represented in terms of profit. The adaptation should eventually relay back to one of the reasons for adapting Agile - for example, faster time to market, increased return on investment through value - based delivery, reduced total cost of ownership through enhanced software quality, and improved customer and employee satisfaction.
Scrum works not because it has three roles, five events, and three artifacts but because it adheres to the underlying Agile principles of iterative, value-based incremental delivery by frequently gathering customer feedback and embracing change. This results in faster time to market, better delivery predictability, increased customer responsiveness, ability to change direction by managing changing priorities, enhanced software quality, and improved risk management.
Do you really need to follow all three Scrum pillars?
To put it briefly, you do. There's a lot to process here, but let's start with transparency. Of the three Scrum pillars, it is the most crucial. If the issue you are facing is unclear, you will undoubtedly inspect and adjust in the incorrect method, further straying from your intended course of action.
Sometimes, you can actually focus only on adapting—simply experimenting with some ideas and brainstorming new ways to develop the product. Then again, it will be necessary to carefully inspect and ask why you’re even trying something new. Maybe your team is bored with the current situation and needs a breath of fresh air?
As you can see, all three pillars are inseparable and strictly connected. You can’t have one without the others.
Working with scrum means developing a cutting-edge product to give your company a headstart on your competition. Scrum is sometimes used to manage projects: a predetermined scope is divided into iterations, and the scope is not intended to be changed while the project is being developed. Before development begins, while knowledge is at its lowest, all decisions are determined. In the event that new information is found throughout the development process, you can wind up wasting money and resources.
Important insights into the product, the market, and the customers that were discovered throughout development have also been purposefully overlooked because doing so would have required going against the original strategy.
Using empiricism and scrum well involves acting quickly to capitalize on learning for the benefit of your clients, business, and market position.































 Link copied!
Link copied!
 Recently Updated News
Recently Updated News