Why Doesn’t South Korea Outsource Its IT Projects Like Other Developed Countries?
Last updated: August 05, 2025 Read in fullscreen view
- 07 Jul 2024
 Top Fintech Companies in Vietnam Driving Innovation Across Digital Banking & Investment 57/133
Top Fintech Companies in Vietnam Driving Innovation Across Digital Banking & Investment 57/133 - 08 Oct 2024
 Vietnam: The Rising Star in Global Outsourcing – Trends and Costs for 2025 32/370
Vietnam: The Rising Star in Global Outsourcing – Trends and Costs for 2025 32/370 - 12 May 2021
 The Real Cost Between Outsourcing IT vs In-House: A Quick Comparison 27/454
The Real Cost Between Outsourcing IT vs In-House: A Quick Comparison 27/454 - 21 Aug 2025
 Top 30 Oldest IT Outsourcing Companies in Vietnam 26/125
Top 30 Oldest IT Outsourcing Companies in Vietnam 26/125 - 11 Mar 2024
 Why You Should Hire Odoo Developers from Vietnam to Customize Your ERP System 25/126
Why You Should Hire Odoo Developers from Vietnam to Customize Your ERP System 25/126 - 24 Nov 2025
 Top Blockchain Companies in Vietnam 24/65
Top Blockchain Companies in Vietnam 24/65 - 14 Aug 2024
 From Steel to Software: The Reluctant Evolution of Japan's Tech Corporates 24/545
From Steel to Software: The Reluctant Evolution of Japan's Tech Corporates 24/545 - 02 Feb 2026
 What Is the Total Cost of Web Development for Small & Medium Businesses? 23/39
What Is the Total Cost of Web Development for Small & Medium Businesses? 23/39 - 03 Oct 2020
 Outsourcing Your MVP Development - Streamlined Solutions for future 23/440
Outsourcing Your MVP Development - Streamlined Solutions for future 23/440 - 22 Mar 2022
 8 Mistakes Marketing Agencies or Consulting Firms Make When Outsourcing Web Development 20/358
8 Mistakes Marketing Agencies or Consulting Firms Make When Outsourcing Web Development 20/358 - 24 Nov 2021
 What is the Actual Cost of Hiring Cheap Developers? 19/392
What is the Actual Cost of Hiring Cheap Developers? 19/392 - 03 Dec 2025
 IT Outsourcing Solutions Explained: What, How, Why, When 19/41
IT Outsourcing Solutions Explained: What, How, Why, When 19/41 - 04 Apr 2024
 Unlock Vietnamese-Japanese outsourcing potential 18/244
Unlock Vietnamese-Japanese outsourcing potential 18/244 - 21 Oct 2021
 Advantages and Disadvantages of IT Outsourcing 17/357
Advantages and Disadvantages of IT Outsourcing 17/357 - 15 Oct 2022
 Project-based team model for one-off and pilot software development projects 16/806
Project-based team model for one-off and pilot software development projects 16/806 - 10 May 2021
 Project Audit and Second Opinion Services 16/258
Project Audit and Second Opinion Services 16/258 - 11 Mar 2023
 Common Pain Points in Software Development Outsourcing 16/260
Common Pain Points in Software Development Outsourcing 16/260 - 31 Oct 2025
 The True ROI of Software Development Outsourcing for Tech Startups 16/88
The True ROI of Software Development Outsourcing for Tech Startups 16/88 - 25 Sep 2025
 A Practical Guide to Secure Online Work for Outsourced Teams 15/90
A Practical Guide to Secure Online Work for Outsourced Teams 15/90 - 05 Jan 2022
 What Outsourcing Engagement Model is Right For You? 15/322
What Outsourcing Engagement Model is Right For You? 15/322 - 14 Dec 2021
 The Top 10 Problems with Outsourcing Implementation and How to Solve Them 15/406
The Top 10 Problems with Outsourcing Implementation and How to Solve Them 15/406 - 15 Aug 2021
 TIGO Rate Formula - Things the partners should know 15/491
TIGO Rate Formula - Things the partners should know 15/491 - 09 Jan 2021
 How can outsourcing enable business agility? 14/202
How can outsourcing enable business agility? 14/202 - 01 Sep 2019
 Outsourcing Software To Vietnam: Facts, benefits and limitations 14/453
Outsourcing Software To Vietnam: Facts, benefits and limitations 14/453 - 07 Nov 2024
 Outsourcing Crisis Looming: Will Trump's Policies Transform the Global IT Landscape? 14/176
Outsourcing Crisis Looming: Will Trump's Policies Transform the Global IT Landscape? 14/176 - 16 Oct 2024
 Building a Software Outsourcing Startup: Strategy Through Two Canvases 13/38
Building a Software Outsourcing Startup: Strategy Through Two Canvases 13/38 - 16 Dec 2021
 Why outsource Python development of your project? 13/474
Why outsource Python development of your project? 13/474 - 12 Jan 2023
 Top 10 Trustworthy IT Outsourcing Companies in Vietnam 13/285
Top 10 Trustworthy IT Outsourcing Companies in Vietnam 13/285 - 19 Mar 2021
 Selective Outsourcing of IT Functions - a new trend in business outsourcing 13/541
Selective Outsourcing of IT Functions - a new trend in business outsourcing 13/541 - 02 May 2021
 Outsourcing Software Development: Avoid 8 Mistakes 12/111
Outsourcing Software Development: Avoid 8 Mistakes 12/111 - 09 Sep 2022
 Close Collaboration and Communication Can Overcome the Challenges of Distributed Teams 12/194
Close Collaboration and Communication Can Overcome the Challenges of Distributed Teams 12/194 - 06 Oct 2021
 Intellectual property issues with outsourcing software development 12/389
Intellectual property issues with outsourcing software development 12/389 - 01 Mar 2022
 Top 5 reasons why outsourcing to Vietnam is a smart move 12/285
Top 5 reasons why outsourcing to Vietnam is a smart move 12/285 - 01 Jan 2024
 Software Outsourcing Questions for 2024 11/157
Software Outsourcing Questions for 2024 11/157 - 03 Nov 2021
 7 phases of Odoo Implementation and Development: Can they be outsourced? 11/406
7 phases of Odoo Implementation and Development: Can they be outsourced? 11/406 - 01 Jan 2024
 Tech Partnerships: Choosing the Right Software Outsourcing Firm in Vietnam 11/181
Tech Partnerships: Choosing the Right Software Outsourcing Firm in Vietnam 11/181 - 01 Jan 2023
 4 New IT Outsourcing Pricing Models to consider in 2023 11/362
4 New IT Outsourcing Pricing Models to consider in 2023 11/362 - 10 May 2021
 What are things you should look for in a good IT outsourcing company? 11/431
What are things you should look for in a good IT outsourcing company? 11/431 - 03 Nov 2022
 Top questions and answers you must know before ask for software outsourcing 11/292
Top questions and answers you must know before ask for software outsourcing 11/292 - 03 Jan 2023
 IT Outsourcing Costs: Is outsourcing really cost-effective? 10/210
IT Outsourcing Costs: Is outsourcing really cost-effective? 10/210 - 05 Aug 2024
 Revisiting the Mistake That Halted Japan's Software Surge 10/342
Revisiting the Mistake That Halted Japan's Software Surge 10/342 - 06 Feb 2026
 How Much Does a CPA Cost for a Small Business? 10/16
How Much Does a CPA Cost for a Small Business? 10/16 - 01 Jan 2024
 12 reasons for software development outsourcing 10/175
12 reasons for software development outsourcing 10/175 - 21 Oct 2022
 Outsourcing Billable Rate 9/270
Outsourcing Billable Rate 9/270 - 01 Jan 2023
 Software Development Outsourcing Trends to Watch Out for in 2023 9/321
Software Development Outsourcing Trends to Watch Out for in 2023 9/321 - 08 Feb 2022
 Software Development: Fixed Cost or Opportunity Cost? 9/468
Software Development: Fixed Cost or Opportunity Cost? 9/468 - 13 Jan 2023
 What are the Hourly Rates in Offshore Software Development? 8/242
What are the Hourly Rates in Offshore Software Development? 8/242 - 04 Jan 2021
 VIETNAM AS A BIG ATTRACTIVE DESTINATION IN THE FIELD OF OUTSOURCING 8/311
VIETNAM AS A BIG ATTRACTIVE DESTINATION IN THE FIELD OF OUTSOURCING 8/311 - 16 Mar 2021
 Outsource Data Engineering Services - TIGO Streamlined Solutions 8/251
Outsource Data Engineering Services - TIGO Streamlined Solutions 8/251 - 08 Aug 2021
 Why Nearshore Software Development is better than In-House Development? 8/199
Why Nearshore Software Development is better than In-House Development? 8/199 - 13 Oct 2021
 Why Outsourcing Software Development Services Is Gaining Traction With Non-Technical Leaders? 8/310
Why Outsourcing Software Development Services Is Gaining Traction With Non-Technical Leaders? 8/310 - 01 Jan 2023
 Top 5 IT outsourcing countries in 2023 7/272
Top 5 IT outsourcing countries in 2023 7/272 - 02 Mar 2021
 Estimate the Cost of Software Development 7/335
Estimate the Cost of Software Development 7/335 - 16 Feb 2026
 Education App Development Cost in 2026: Benchmarks and Key Cost Drivers 7/13
Education App Development Cost in 2026: Benchmarks and Key Cost Drivers 7/13 - 01 Jun 2025
 10 Sustainable & Unique IT Outsourcing Companies in Vietnam 6/79
10 Sustainable & Unique IT Outsourcing Companies in Vietnam 6/79 - 15 Nov 2023
 IT Staff Augmentation Types and the Best Choice for Your Business 6/190
IT Staff Augmentation Types and the Best Choice for Your Business 6/190 - 10 Jan 2024
 Facts Chart: Reasons for outsourcing 6/152
Facts Chart: Reasons for outsourcing 6/152 - 21 Aug 2022
 Forbes: IT Outsourcing Hotspot: Vietnam, A Small But Mighty Powerhouse 6/257
Forbes: IT Outsourcing Hotspot: Vietnam, A Small But Mighty Powerhouse 6/257 - 10 Mar 2021
 The 7 Biggest Mistakes to Avoid Before Outsourcing a Web Development Project 6/237
The 7 Biggest Mistakes to Avoid Before Outsourcing a Web Development Project 6/237 - 12 Oct 2021
 Vietnam outsourcing path - the silk road connecting ASEAN with the developed countries (EU, US, Japan...) 6/302
Vietnam outsourcing path - the silk road connecting ASEAN with the developed countries (EU, US, Japan...) 6/302 - 17 Oct 2020
 How Outsourcing can Improve Time Management for Better Business 6/270
How Outsourcing can Improve Time Management for Better Business 6/270 - 19 Oct 2020
 The hidden costs of outsourcing software development 6/449
The hidden costs of outsourcing software development 6/449 - 25 Nov 2021
 Low-Cost Software Development: Buy Nice or Buy Twice? 6/338
Low-Cost Software Development: Buy Nice or Buy Twice? 6/338 - 28 Oct 2022
 Expect the unexpected in 2023 - How Outsourcing Can Help? 6/199
Expect the unexpected in 2023 - How Outsourcing Can Help? 6/199 - 01 Oct 2022
 Vietnam is a favorite supply of IT outsourcing services to Japan 5/234
Vietnam is a favorite supply of IT outsourcing services to Japan 5/234 - 01 Jan 2023
 Why is Vietnam the Top IT Outsourcing Destination of 2023? 5/234
Why is Vietnam the Top IT Outsourcing Destination of 2023? 5/234 - 17 Jan 2024
 What are the benefits and challenges of using multi-sourcing or single-sourcing strategies? 5/187
What are the benefits and challenges of using multi-sourcing or single-sourcing strategies? 5/187 - 01 Jan 2024
 Hiring Tech Talents in Asia: An Overview of Skills, Costs, and Potential 5/162
Hiring Tech Talents in Asia: An Overview of Skills, Costs, and Potential 5/162 - 02 Nov 2023
 What are the pros and cons of iIT outsourcing? 5/189
What are the pros and cons of iIT outsourcing? 5/189 - 01 Jan 2023
 Top Software Development Challenges in 2023 5/298
Top Software Development Challenges in 2023 5/298 - 01 May 2023
 Streamline Your Business with Outsourcing 5/193
Streamline Your Business with Outsourcing 5/193 - 01 Apr 2021
 IT Outsourcing to vietnam: Why It Is A Good Choice? 5/292
IT Outsourcing to vietnam: Why It Is A Good Choice? 5/292 - 01 Jan 2024
 What The World Is Flat Means to IT Outsourcing 4/166
What The World Is Flat Means to IT Outsourcing 4/166 - 08 Jan 2024
 Outsourcing on an As-Needed Basis 4/158
Outsourcing on an As-Needed Basis 4/158 - 01 Feb 2023
 [InfoWorld] Is your outsourcer agile enough? 4/193
[InfoWorld] Is your outsourcer agile enough? 4/193 - 15 Aug 2025
 Quantum Technology: Global Challenges and Opportunities for Innovators 4/100
Quantum Technology: Global Challenges and Opportunities for Innovators 4/100 - 31 Dec 2021
 Outsourcing Software Development to mitigate the impact of COVID-19 2/320
Outsourcing Software Development to mitigate the impact of COVID-19 2/320
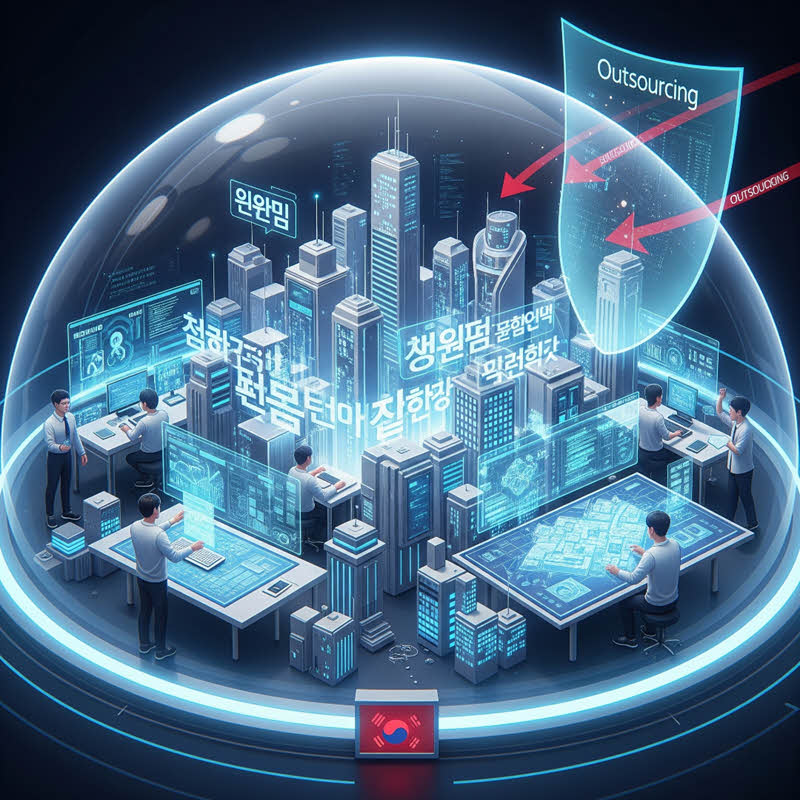
While many developed countries such as Japan have actively outsourced IT projects to lower-cost countries like Vietnam, India, and the Philippines, South Korea appears largely resistant to this global trend. Why is that?
This raises several questions about a nation that is growing rapidly—now surpassing Japan in GDP per capita:
- As a high-tech country, does South Korea face an IT talent shortage?
- With relatively high domestic labor costs, why doesn't it cut costs through outsourcing?
- Are there cultural, linguistic, or internal strategic barriers that drive companies to develop in-house instead of collaborating externally?
- What are the key reasons why Korean businesses avoid IT outsourcing?
Based on our consulting experience at TIGO with troubleshooting ERP systems customized for Korean factories, several deep-rooted factors may explain this pattern:
1. Self-Reliance and Information Security
Korean corporate culture places strong emphasis on internal control and data confidentiality. Major corporations such as Samsung, LG, and Naver maintain strong in-house IT departments and avoid sharing core data externally. Outsourcing is often seen as a risk—either for leaking technological secrets or losing internal control.
2. Language and Cultural Barriers
Korean is not a widely spoken language, and Korean companies primarily operate in their native tongue. They do not commonly use English in technical communications, which creates significant difficulties in collaborating with global outsourcing teams. Unlike Japan, Korea has made fewer efforts to “internationalize” its technical teams.
3. Investment in Domestic Talent
South Korea heavily invests in training local engineers and developing strong partnerships between tech universities and businesses. This strategy has helped create a stable pipeline of domestic IT talent, reducing dependency on external resources.
At events like K-Innovation, Korean companies showcase hundreds of high-tech solutions developed by Korean engineers. Very few of these solutions are outsourced to other countries.
4. In-House Technology Development Strategy
South Korea tends to build everything in-house—from hardware to software. With a long-term vision to become a global leader in AI, 5G, robotics, and more, maintaining in-country development capacity is a core part of the national strategy.
5. Proprietary Software and Database Ecosystems
Unlike many countries that rely on global database systems such as Oracle, MS SQL, or PostgreSQL, Korean businesses often develop their own “made-in-Korea” database systems. When expanding abroad, they bring their entire proprietary ecosystem instead of adopting local or international platforms. This makes outsourcing nearly impossible, as there is little documentation or external expertise available. In fact, hiring foreign engineers to customize these systems often costs more than using local talent, due to the need for additional training and familiarization.
6. Lean and High-Productivity Operations
Korean IT companies are known for being extremely lean and efficient. Many are able to build large-scale software systems with teams of fewer than ten developers. The “work hard – deliver fast” culture is deeply embedded in their work processes and discipline. As a result, if internal capacity is sufficient, there's little need to expand with external resources.
7. Conclusion
Is South Korea going against the tide of global IT outsourcing to preserve its “technological identity”? Or is this a strategic move to strengthen domestic capabilities in the era of global tech competition?
However, the golden era of Korea’s IT industry may not last long amid rapid and profound global technological shifts. The rise of AI, large language models (LLMs), low-code/no-code (LCNC) platforms, and new development paradigms such as “vibe coding” is fundamentally changing how digital products are created.
Moreover, powerful and affordable solutions like Odoo, ERPNext, Zoho, and Larksuite are increasingly dominating the enterprise world thanks to their open, flexible, and integrable nature. In contrast, Korea’s closed and locally-oriented software ecosystem is at risk of falling behind if it does not adapt to the more open and collaborative trends.
As the world moves toward global cooperation, even the most efficient closed systems risk isolation. Without strategic shifts—both technologically and organizationally—South Korea may find it increasingly difficult to stay competitive.
Pham Dinh Truong
TIGO CONSULTING































 Link copied!
Link copied!
 Recently Updated News
Recently Updated News